Transport Pipeline in Exchange Server 2019
In this article we will dive deep into Transport Pipeline in Exchange Server and we will understand how Transport Pipeline works in Exchange Server 2019.
This is the 7th article of Exchange Server 2019 and Exchange Hybrid series. Please refer to below links if you want to go through the previous articles:
Install Active Directory on Windows Server 2019 and promote to Domain Controller
DNS records in Active Directory
Demystifying Exchange Server: Roles, Architecture, and Functionality Explained
Exchange Server 2019 prerequisites
Install Exchange Server 2019 on Windows Server 2019. A step by step Guide
How to configure Exchange Server 2019 post installation
Table of Contents
Watch video
Join our YouTube channel and explore Transport Pipeline in Exchange Server 2019 video for a deep dive session.
How email flow works in Exchange Server
Before we talk about Transport Pipeline, let’s look at a high-level picture of email flow in Exchange Server.
Inbound email flow
When an email is sent from Internet to your on-premise Exchange Server organization, a receive connector on Front End Transport Service receives that email.
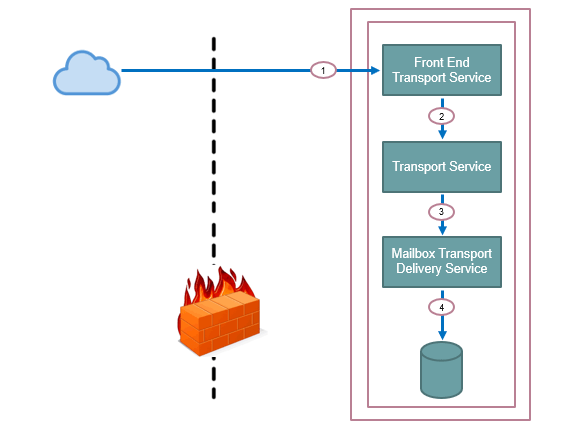
Then few checks are performed on this email like, transport rules, anti-spam, and anti-malware checks. When this email is passed from these checks, it is forwarded to the Transport Service. Few checks are performed here as well like, recipient resolution, routing resolution, and bifurcation.
And then this email is forwarded to Mailbox Transport Delivery Service and this service delivers the email to the mailbox database.
Outbound email flow
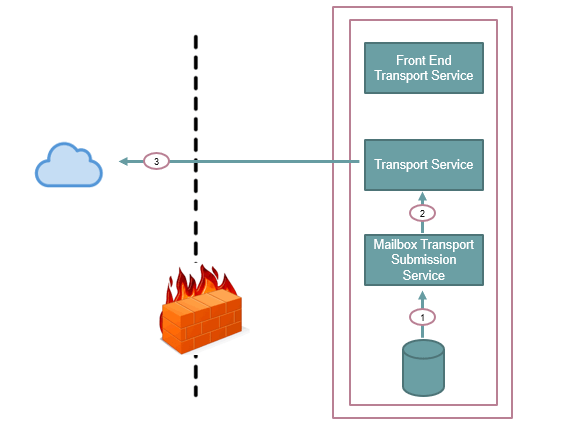
If we talk about Outbound email flow, when a user sends email from his email application, the email is picked up by Mailbox Transport Submission service. It forwards that email to the Transport Service, and then this email is sent to the internet through an outbound connector.
But the above pictures are not enough to understand the background process of the email flow in Exchange Server. If you want to know the background process, then we need to understand the concept of Transport Pipeline.
What is Transport Pipeline in Exchange Server
Transport pipeline is a collection of services, connectors, components and queues, those work together to manage email routing in an Exchange server organization.
Components of Transport Pipeline
Before we deep-dive into transport pipeline, let’s understand what are the different components of transport pipeline those help in managing email routing.
In Exchange 2019, transport pipeline has 4 components.
1. Front-End Transport Service
2. Transport Service on Mailbox server
3. Mailbox Transport Service
4. Transport Service on the Edge Transport server
Front-End Transport Service: Front-End transport service runs on the mailbox server. This service works like a proxy service for all inbound and outbound external SMTP traffic for the Exchange organization. This service accepts the SMTP connections from the other SMTP servers on the internet, it receives emails, and initiates SMTP connections for email sending. This services doesn’t inspect email contents. But this service can filter the emails on the basis of IP connections, domains, senders and recipients.
Transport Service on Mailbox Server: This service also runs on the mailbox server. This service is similar to the Hub Transport Server role that existed in Exchange Server 2010. Transport Service handles the internal mail flow within Exchange organization. This service has further components, those help this service to handle the email routing.
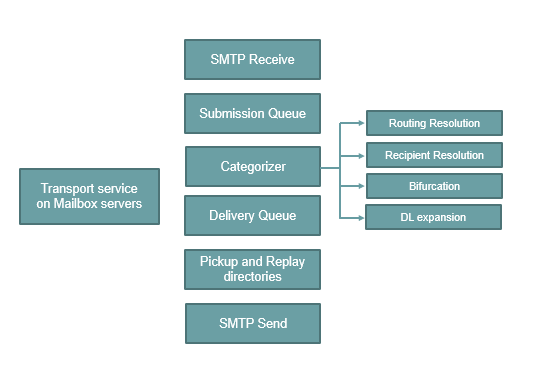
- SMTP Receive: The first component of Transport Service is SMTP Receive. When emails are received by the Transport Service, a series of multiple processes is performed to validate that email. This includes, message-content inspection, Transport Rules, Anti-Spam and Anti-Malware inspection. Once the email is passed from SMTP Receive and is not rejected by any of the anti-spam agents or anti-malware agents, SMTP receive places that email in the submission queue.
- Submission Queue: Submission is the process of putting the emails into the submission queue. The submission queue stores all the emails on a disk until the categorizer processes them for delivery. While categorizer processes an email, a copy of the email remains in the submission queue. After the email is successfully processed, the Transport service removes the email from the categorizer and the Submission queue.
- Categorizer: Categorization is the process that is responsible for all the routing decisions. The categorizer performs 4 important tasks Routing Resolution, Recipient Resolution, Bifurcation, and DL expansion. The categorizer processes all the emails and decides what to do with each email based on its destination. It retrieves the emails from the Submission Queue, processes them and delivers the emails to the delivery queue. When an email is received, categorizer matches the email address of the recipient with an associated object in Active Directory. If match is not found, the email is rejected and it generates an NDR or Non-Delivery-Report.
- Delivery Queue: Delivery Queue contains the emails those are not delivered to the recipients because of any reason. It could be recipient not found, transport service is not available, or any other reason.
- Pickup and Replay Directories: Next component of Transport Service is Pickup and Replay Directories. The pickup directory is used by the administrators for mail flow testing or by the applications that create and submit their own emails. And the replay directory receives messages from 3rd party gateway servers and can also be used to resubmit emails that administrators export from the queues of Exchange servers.
- SMTP Send: SMTP Send component is used to send emails to the recipients. The recipient can be located on the same mailbox server or it can be located on a different mailbox server that is part of the same Database Availability Group (DAG) or it can be on Internet.
Mailbox Transport Service: This service runs on the mailbox server. Mailbox Transport Service has further 2 services, Mailbox Transport Delivery Service and Mailbox Transport Submission Service.
- Mailbox Transport Delivery Service: Mailbox Transport Delivery Service has a component called Store Driver Deliver Service. This service delivers the emails to the mailbox database.
- Mailbox Transport Submission Service: Mailbox Transport Submission Service has a component called Store Driver Submission Service. This service retrieves the emails from the sender’s outbox and submits those emails to the Submission Queue. Once these emails are submitted to the Submission Queue, it moves the emails from the sender’s outbox to the Sent Items folder.
Transport Service on Edge Transport server: This service is very similar to the Transport Service that runs on the mailbox server. If you have an Edge Transport server installed in the perimeter network, all the emails coming from the Internet or going to the Internet, flows through the Transport Service that runs on the Edge Transport server.
Transport Pipeline in Exchange Server
Now let’s understand how email flow works in Exchange Server and how each component that we discussed above plays an important role in email flow.
Transport Pipeline in Inbound Email Flow
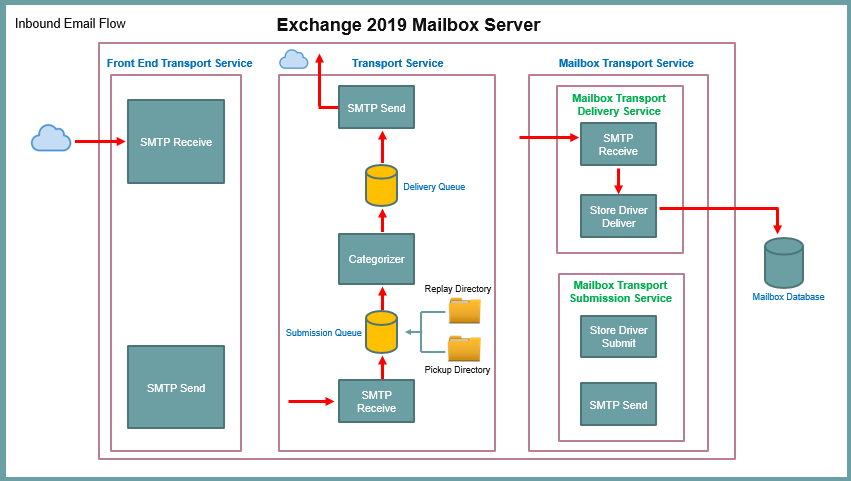
When an email is sent from the Internet to an Exchange server organization, the email is accepted by the Receive Connector on Front End Transport Service.
Then this email is handed over to the SMTP Receive component of the Transport Service. On this level, few checks are performed on that email. For example, Transport Rules, Anti-Spam and Anti-Malware checks. If this email is passed from these checks, then this email is submitted to the Submission Queue.
Then Categorizer picks that email from the Submission Queue. It will first verify if the destination email address is correct (recipient resolution). If this email is sent to a distribution group, in that case categorizer will expand the DL (DL expansion) so that it can identify the email address of the each member.
Then categorizer will perform Routing Resolution. That means it will identify if the recipient is internal or it is external. And then it will hand over the email to the Delivery Queue. During Routing Resolution if recipient is found as an external user, in that case the email will routed to the Internet through a Send connector. And if recipient is internal, then this email will be forwarded to Store Driver Deliver Service that runs on the Mailbox Transport Delivery Service. And Store Driver Deliver Service will deliver this email to the mailbox database and this email will be delivered to the user’s mailbox.
Transport Pipeline in Outbound Email Flow
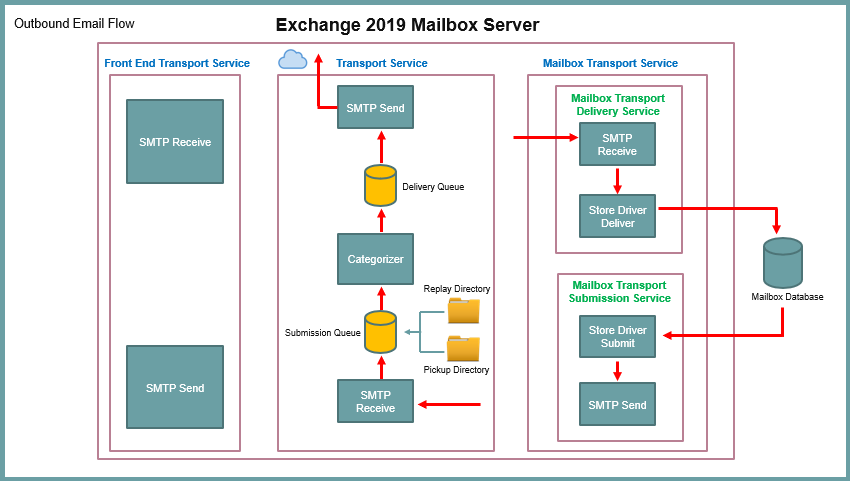
If a user sends email from Exchange organization, Store Driver Submission Service picks that email from the user’s Outbox and it submits that email to the Submission Queue.
Categorizer picks that email from the Submission Queue, it performs Routing Resolution, Recipient Resolution, Bifurcation, and if email is sent to a distribution list it expands the DL to check all the members of that DL. After these checks, Categorizer forwards that email to the Delivery Queue.
If recipient is external, the email will be routed to the Internet through a Send Connector. And if recipient is internal, the email will be handed over to the Store Driver Deliver Service that delivers the email to the mailbox database.
So this is how email flow works in Exchange Server.
Conclusion
In this article we learnt what is Transport Pipeline in Exchange Server, we discussed the components of Transport Pipeline, and you learnt how inbound and outbound mail flow works in Exchange Server.
Found this article helpful and informative? You may also like A Deep Dive session into Autodiscover. Please share this article within your community, follow us on our YouTube channel and join our Newsletter for early updates and articles.
Related articles
We welcome you to browse our articles on Exchange Online:
Google Workspace to Microsoft 365 Migration
Microsoft 365 Tenant to Tenant Migration. A Comprehensive Guide to Mailbox Migration.
Sophos Central Email Security integration with Exchange Online – Step by step guide.
Demystifying Autodiscover. A Deep Dive into Autodiscover.
Troubleshooting Inbound connector in Exchange Online
Troubleshooting Exchange Online Mail Flow: A Comprehensive Guide
Exchange Online Protection (EOP) interview questions and answers
Demystifying the High Risk Delivery Pool (HRDP) in Exchange Online
Exploring the Power of Public Folders in Exchange Online, Office 365 and Microsoft 365
50+ Exchange Online Mail Flow Interview questions and answers
Happy Learning!!
