40+ Exchange Hybrid Interview questions and answers
Hi Guys and welcome to Office 365 Concepts. If you are preparing yourself for an interview in Exchange Hybrid project, this is the right place to start with. These Exchange Hybrid interview questions and answers will help you to prepare yourself for the technical round.
Top 10 frequently asked Exchange Hybrid Interview questions and answers
- What is Exchange Online?
- What is Exchange Hybrid deployment?
- What are the pre-requisites for Exchange Hybrid deployment?
- What is Unified GAL in Exchange Hybrid?
- Tell me about any 5 benefits of Exchange Hybrid deployment?
- What is Centralized Mail Flow in Exchange Hybrid?
- What is the difference between Target Address and Remote Routing Address?
- Which services in Exchange Server are responsible for Mailbox Migration in Exchange Hybrid deployment?
- What is the difference between on-boarding and off-boarding in Exchange Hybrid?
- Is mailbox migration a pull process or push process in Exchange Hybrid?
Exchange Hybrid Interview questions and answers for L2 role.
1. What is Exchange Online?
Exchange Online is a cloud-based messaging platform that provides access to features like calendar, emails, address book, contacts, and tasks. Once you have supported Exchange Online license, you can access your emails and calendar through Outlook desktop client, mobile app, or from OWA (Outlook on the Web).
2. What is Exchange Hybrid deployment?
Exchange Hybrid deployment is a model where 2 different organizations (Office 365 and on-premises Exchange server) are combines together to form a single organization. You can move mailboxes from EXO to on-premise and vice-versa, you can share calendars, cross-premises permissions and much more.
3. What are the pre-requisites for Exchange Hybrid deployment?
- We need to make sure we are using the supported Exchange version for hybrid server. Exchange Server 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019 with latest CU installed. (If not latest then it should be immediate previous).
- We need Office 365/M365 tenant with supported subscription. (Home plans and Microsoft 365 Apps for business plans are not supported, rest all plan are supported).
- Custom domain that we are using in on-premises Exchange Server, that should be added and verified in Office 365.
- We need to deploy Azure AD Connect (Microsoft Entra Connect) in on-premise environment.
- Configure Autodiscover record for your domain in public DNS that points to on-premise Exchange Server.
- We need SSL certificate provided by 3rd party certification authority. And, autodiscover endpoint and EWS URL for on-premise Exchange Server should be added in Subject Alternate Name (SAN) field in certificate.
4. What is Unified GAL in Exchange Hybrid?
Unified GAL includes Exchange Online recipients and the mail-users those are the mailboxes synced from on-premises Exchange server in Exchange Hybrid deployment.
5. Any 5 benefits of Exchange Hybrid deployment?
- Same domain namespace. Exchange on-premise and Exchange Online users use same domain for their email addresses and UPNs.
- Unified GAL. Unified GAL includes Exchange Online recipients and the mail-users those are the mailboxes synced from on-premise in Exchange Hybrid deployment.
- Centralized Mail Flow. In centralized mail flow, we can control the routing of emails from on-premises Exchange Server.
- Free/Busy. On-premise Exchange and Exchange Online users can check each other’s free/busy availability.
- Cross-premises permissions. We can assign mailbox permissions to the on-premise Exchange user for a user that exists in Exchange Online and vice-versa.
6. What is Centralized Mail Flow in Exchange Hybrid?
Centralized mail flow is a feature of Exchange Hybrid deployment that helps Administrators to manage email flow from on-premise Exchange Server.
Scenario: When centralized mail flow is enabled and MX record points to EOP (Exchange Online Protection), any external email will first be delivered to EOP, and with the help of Outbound Connector in EOP that email will be routed to on-premise. And then recipient resolution will be done, if recipient exists in on-premise, email will be delivered to the user, if recipient exists in EXO, the email will be routed from on-premise Exchange to EOP with the help of Send Connector in Exchange Server, and then email will be delivered to the mailbox in EXO.
7. What is the difference between Target Address and Remote Routing Address?
Target Address is used for the Autodiscover lookup in Exchange Hybrid. Remote Routing Address routs incoming queries for the on-premise Mailbox to Exchange Online. Remote Routing Address tells any incoming query that the mailbox has been migrated to Exchange Online.
8. Which services in Exchange Server are responsible for Mailbox Migration in Exchange Hybrid deployment?
MRS Proxy service and Migration Service.
9. What is the difference between on-boarding and off-boarding in Exchange Hybrid?
Onboarding is the migration process to migrate a mailbox from on-premise Exchange Server to Exchange Online. Offboarding is the migration process to migrate Exchange Online mailbox to on-premise.
10. Is mailbox migration a pull process or push process in Exchange Hybrid?
In Exchange Hybrid if we are migrating a mailbox from EXO to on-premise or from on-premise to EXO, the complete migration process is managed through Exchange Online. If we are migrating a mailbox from on-premise Exchange to Exchange Online, this will a pull process. If we are migrating a mailbox from Exchange Online to On-premise Exchange Server, this will be a push process.
11. What is the difference between Staged migration and Cutover migration?
If you are using Exchange Server 2003 or 2007, you can use Staged Migration to migrate mailboxes from on-premise Exchange to Exchange Online. In staged migration, you need to deploy Azure AD Connect server in your on-premise environment.
If you are using Exchange Server 2003 or later, you can use Cutover migration. Cutover migration does not require Azure AD Connect deployment.
12. What is Hybrid Configuration Wizard (HCW)?
Hybrid Configuration Wizard (HCW) is a tool that validates and configures a seamless connection between on-premise Exchange Server and Exchange Online and enables all the hybrid features (depending on the topology selected).
13. How many roles are available in Exchange Server 2019?
Exchange Server 2019 has 2 roles. Mailbox and Edge Transport.
14. How many roles are available in Exchange Server 2010?
Exchange Server 2010 has 5 roles. Mailbox, Client Access Server (CAS), Unified Messaging, Hub Transport, and Edge Transport.
15. What is an Organization Relationship in Exchange Hybrid deployment?
An organization relationship is a on-to-one relationship between 2 organizations (Exchange Server and Exchange Online) that allows users to share their calendars and free/busy information with each other.
16. What is the format of Remote Routing Address in Exchange Hybrid?
username@domain.mail.onmicrosoft.com
17. Which service is responsible for the working of cross-premises permissions in Exchange Hybrid?
Autodiscover and EWS.
18. Where do we point MX record in Exchange Hybrid deployment?
You can point MX record to either on-premises Exchange server or Exchange Online Protection. But the recommended configuration is to point MX record to EOP (Exchange Online Protection) in Exchange Hybrid deployment. So that all incoming emails will be filtered by EOP and then delivered to recipients.
19. If we are using 3rd party email filter server, where would we point MX record for Office 365 domain?
If you are using 3rd party email filter server, then you should point MX record to 3rd party email filter server.
20. What is the difference between “Partner Organization” and “Your Organization’s email server” connector?
Both type of connectors are outbound connectors and are created in EOP. When we want to route emails to a 3rd party email server, we create Partner Organization connector. When we want to route emails from EOP to on-premise Exchange Server, we create Your Organization’s email server connector.
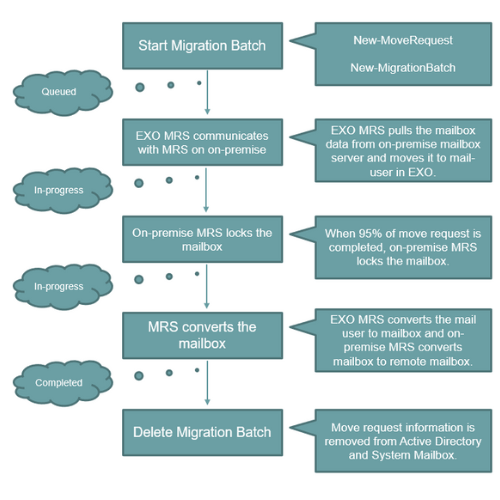
21. Explain backend process of Remote Move (Hybrid) migration from on-premise to Exchange Online?
When we start a migration batch a PowerShell command New-MigrationBatch is initiated at the background. If you initiate migration from PowerShell command using New-MoveRequest, in that case the same command will be initiated in the background. At this point, the move request status will show as Queued. That means the migration request is in the queue.
In step 2, Exchange Online Mailbox Replication Service or MRS communicates with MRS service that is running on the on-premise Exchange Server. The Mailbox Replication Service in Exchange Online pulls the mailbox data from the on-premise mailbox server, and it moves the data to the mail-enabled mail-user in Exchange Online. At this point, migration status will be in-progress.
When the move request is 95% completed, the on-premise Mailbox Replication Service locks the on-premise mailbox till the final synchronization is completed. At this point of time, the move request status is still in-progress.
In step 4, Exchange Online Mailbox Replication Service converts the mail-enabled mail-user to a mailbox. And in on-premise, Mailbox Replication Service converts the mailbox to mail-enabled remote mailbox. And the actual on-premise mailbox is soft-deleted. And the move request status shows completed.
In step 5, the administrator deletes the migration batch from Exchange Online. And the move request information is cleared from Active Directory and from the system mailbox.
To learn more about backend process in Remote Move migration, refer to this video.
22. While migrating a mailbox from on-premise to Exchange Online in Remote Move, we are getting error “his mailbox exceeded the maximum number of large items”. What will be your course of action to fix this?
To fix this issue, find and remove messages that are larger than 150 MB from the user’s on-premises mailbox. Login to Outlook and sort emails from largest to smallest. Take backup of mailbox in a PST file, and delete emails those are larger than 150MB. Try migrating the mailbox again.
23. What do you understand with Arbitration Mailbox?
Arbitration mailbox is a system mailbox that stores different type of information like, information about migration objects (migration endpoint, migration batches and migration users), messaging approval workflow and information about audit logs.
24. What is Microsoft Federation Gateway?
Microsoft Federation Gateway is a free cloud-based service that acts as a trust broker between on-premise Exchange Server and Exchange Online. When you create an Office 365 tenant, a trust is automatically created between Office 365 and Microsoft Federation Gateway. But for on-premise Exchange Server, this trust is not created automatically. This trust is created when you run Hybrid Configuration Wizard or you can create it manually using PowerShell commands.
25. What is the difference between Originating and Incoming email directionalities?
Originated: An email is that is originated (sent) from on-premise email server or from Exchange Online tenant.
Incoming: When an email is sent to one of the accepted domains of your Tenant, email directionality will be incoming.
26. What attribute is responsible to route all emails from EOP to on-premise Exchange when centralized mail flow is enabled?
When Centralized Mail Flow is enabled, the Outbound Connector‘s attribute RouteAllMessagesViaOnPremises is set to True. This attribute is responsible to route emails from EOP to on-premise Exchange Server when Centralized mail flow is enabled.
27. What is the difference between Target Address and Remote Routing Address?
Target Address is used for the autodiscover queries and to route emails to EOP. Remote Routing Address tells any incoming query that the mailbox has been migrated to Office 365.
28. What are virtual directories in Exchange Server?
A virtual directory is used by Internet Information Services (IIS) to allow access to a web application such as Exchange ActiveSync, Outlook Web App, or the Autodiscover service.
29. Which services in Exchange Server are responsible for Mailbox Migration?
Mailbox Replication Service (MRS) and Migration Service.
30. What components are involved in Exchange Hybrid deployment?
Exchange Hybrid Deployment includes 5 components.
- Exchange Server: The first component is Exchange Server. If you want to deploy Exchange Hybrid, you need at least one Exchange Server in your environment. If you have Exchange 2016 or 2019, you need at least one Mailbox Server. And if you have Exchange 2013 or earlier version, you need at least one Mailbox Server and one Client Access Server.
- Office 365 Tenant: The second component of Exchange Hybrid deployment is Office 365 tenant. Office 365 is a cloud-based subscription model. This is also called Software as a Service. (Where you use services based on the subscription that you have purchased).
- Microsoft Federation Gateway (MFG): The 3rd component of Exchange Hybrid Deployment is Azure Active Directory Authentication System or Microsoft Federation Gateway (MFG). This is a free cloud-based service that acts as a trust broker between on-premise Exchange Server and Exchange Online. When you create an Office 365 tenant, a trust is automatically created between Office 365 and MFG. But for on-premise Exchange Server, this trust is not created automatically. This trust is created when you run Hybrid Configuration Wizard or you can create it manually using PowerShell commands.
- Azure AD Connect: The 4th component of Exchange Hybrid Deployment is Azure AD Connect. Azure AD Connect is a Microsoft tool that is used to synchronize on-premise identities to Office 365.
- Hybrid Configuration Wizard: And the 5th component of Exchange Hybrid deployment is Hybrid Configuration Wizard or HCW. Hybrid Configuration Wizard provides a streamlined process to configure an Exchange hybrid deployment between on-premise Exchange and Exchange Online.
31. What is EWS (Exchange Web Services) virtual directory in Exchange?
EWS virtual directory provides features like, calendar sharing with external users, free/busy, out of office messaging, and connecting 3rd party applications with the client’s mailbox.
32. What is an Organization Relationship?
An organization relationship is a one to one relationship between 2 organizations that is used to share free/busy or calendar information with each other.
33. Scenario: UserA in on-premise Exchange wants to see free/busy availability of a migrated user UserB. How this free/busy look up with work?
UserA will create a meeting from outlook or from OWA, and he will add UserB as an attendee within the scheduling assistant. On-premise exchange server will find that UserB has a target address that is pointing to domain.mail.onmicrosoft.com and this mailbox is not in on-premise. Exchange Server has a service that is called Availability Service, that is responsible to provide up-to-date information of free/busy. Availability service will try to find a path, to query UserB’s free/busy information from office 365.
Availability Service will first check if on-premise exchange server has Intra-Organization Connector with domain name domain.mail.onmicrosoft.com. If there is no intra-organization connector, then availability service will look for Organization Relationship that is configured with domain name domain.mail.onmicrosoft.com.
Suppose there is no Intra-Organization Connector and Organization Relationship. In that case, availability service will look for Availability Address Space. Availability address space has a domain name set to domain.mail.onmicrosoft.com that is used for free/busy looks when there is no organization relationship or Intra-Organization connector.
Let’s assume the on-premise exchange server has Organization Relationship. Availability service will check the organization relationship and will look for ApplicationURI attribute that is set to Outlook.com. Outlook.com is an identifier for the office 365 organization trust in Microsoft Federation Gateway.
At this point availability service has found how it can reach office 365 organization where UserB’s mailbox is located. Availability service will request MFG for a delegation token so that it can communicate with Office 365.
When exchange server will receive a delegation token from MIcrosoft Federation Gateway (MFG), it will send an autodiscover request to exchange online. This request is sent on the url that is mentioned within Target Autodiscover EPR attribute of Organization Relationship.
If autodiscover request is passed, on-premise exchange will make an EWS request to exchange online along with delegation token. This EWS request is made for UserB’s free/busy availability.
Exchange online will check and validate the delegation token that was issued to on-premise organization by MFG. Once this token is verified, exchange online will return free/busy information of UserB’s mailbox. And then UserA will be able to see whether UserB is free or he is busy during that time.
34. Which service is responsible for cross-premises permissions in Exchange Hybrid?
Exchange Web Services (EWS) and Autodiscover.
35. What is Categorizer in Transport Pipeline?
Categorizer is responsible for the routing decisions. It does Routing Resolution, Recipient Resolution, Bifurcation, and DL expansion.
When an email is received, categorizer matches the email address of the recipient with an associated object in Active Directory. If match is not found, the email is rejected and it generates an NDR or Non-Delivery-Report.
Bifurcation is the process when same email is sent to 2 or more users those are in located different sites. Categorizer checks the path to route that email. It creates a direct connection to the Hub Transport Service that is close to the recipient’s mailbox server. This is called bifurcation.
Categorizer expands the distribution list so that each recipient can be identified who belongs to the distribution list.
36. We are migrating a mailbox from on-premise Exchange to Exchange Online in Hybrid Migration, but we are getting error “the target mailbox doesn’t have an SMTP proxy matching contoso.mail.onmicrosoft.com”. What could be the issue and what resolution you can suggest us?
This issue may occur if the source mailbox (on-premise mailbox) doesn’t has domain.mail.onmicrosoft.com SMTP address stamped. You can run Get-Mailbox “affected user” | fl to verify if the user has this email address added or not. If this email address is not added, you can add it from Exchange Server in mailbox properties and synchronize the user again to Azure AD. If this value is added already, we need to verify if this value is synchronized to Microsoft 365 or not.
37. What is Service Connection Point (SCP) ?
When we install Exchange Server, a Service Connection Point (SCP) object is created in Active Directory. This Service Connection Point object contains 2 important attributes. Service Binding Information and Keywords.
Service binding information attribute stores the Fully Qualified Domain Name or the FQDN of Client Access Services. And the format of Service Binding Information attribute is https://autodiscover.domain.com/autodiscover/autodiscover.xml
Keywords attribute stores the name of the Active Directory site where the mailbox server is installed. In case of Exchange Server 2016 and 2019, this will be the mailbox server, and in case of Exchange 2013 or 2010, this will be the Client Access Server.
38. In Exchange Hybrid deployment, if an on-premise user sends an email to a migrated user, how this email flow will work?
When on-premise user will send email to a migrated user, this request will be accepted by on-premise Exchange Server. With the help if remote routing address, Exchange Server will identify that this user is migrated to Exchange Online. Exchange Server will use Hybrid domain namespace of the recipient and the email will be routed to Exchange Online. Exchange Online will do recipient resolution and email will be delivered to the mailbox.
39. What is Hybrid domain namespace?
Hybrid domain namespace is used by on-premise Exchange Server to route Emails and Autodiscover queries to Exchange Online for the migrated users.
Format of Hybrid domain namespace is domain.mail.onmicrosoft.com, where domain is the domain name added in on-premise Exchange Server in accepted domains and verified in Office 365 tenant.
40. What tasks are performed in the background when you run HCW?
Please refer to this link to learn the background process of Exchange Hybrid Configuration Wizard (HCW).
41. What is hybrid in Exchange?
In the realm of Microsoft Exchange, a hybrid deployment refers to a configuration that combines on-premises Exchange servers with Exchange Online, an integral part of Microsoft 365 (formerly known as Office 365). This setup enables organizations to seamlessly integrate their on-premises infrastructure with cloud-based services.
Here are some key features of a hybrid Exchange deployment:
- Coexistence: It allows simultaneous operation of users in both on-premises and Exchange Online environments within the same organization. This means that certain users can have mailboxes hosted on-premises, while others can have their mailboxes in the cloud.
- Cross-premises functionality: Hybrid Exchange deployments ensure smooth integration between on-premises and Exchange Online environments. Users can benefit from features such as calendar sharing, mail flow, and unified global address lists, irrespective of their mailbox location.
- Migration flexibility: Organizations can gradually migrate their mailboxes using hybrid deployments. They have the flexibility to move mailboxes from on-premises servers to Exchange Online at their own pace, without causing disruption to user productivity.
- Exchange management: The familiar tools used for managing on-premises Exchange infrastructure, such as the Exchange Admin Center (EAC) or PowerShell, can continue to be used in hybrid deployments. These management capabilities are extended to include the Exchange Online environment as well.
- Enhanced scalability and resilience: By leveraging the cloud-based Exchange Online infrastructure, organizations can benefit from improved scalability and resilience. Exchange Online provides high availability, automatic updates, and robust security features.
Hybrid deployments are commonly utilized by organizations as they transition from an on-premises Exchange environment to a cloud-based solution. They offer a flexible and phased approach to migration, ensuring interoperability between both environments.
FAQ
What is hybrid in Exchange?
In the realm of Microsoft Exchange, a hybrid deployment refers to a configuration that combines on-premises Exchange servers with Exchange Online, an integral part of Microsoft 365 (formerly known as Office 365). This setup enables organizations to seamlessly integrate their on-premises infrastructure with cloud-based services.
Related blogs
We welcome you to browse our other articles on Interview Questions & Answers and Microsoft Exams:
SC-900 Exam Questions and Answers
MS-203: Microsoft 365 Messaging: Questions and Answers
Exam MS-102: Microsoft 365 Administrator questions and answers
Top 50+ Office 365 Interview questions and answers
40+ Exchange Hybrid Interview questions and answers
50+ Exchange Online Mail Flow Interview questions and answers
50+ Microsoft Exchange Server Interview Questions and Answers
40+ Azure AD Connect Interview Questions and Answers
50+ Microsoft Exchange Online interview questions and answers
Happy Learning!!
