Demystifying Exchange Server: Roles, Architecture, and Functionality Explained
This is the 3rd blog of Exchange Server 2019 and Exchange Hybrid series. Please refer to below links if you have missed the previous blogs:
Install Active Directory on Windows Server 2019 and promote to Domain Controller
What is DNS and DNS records in Active Directory
In this blog we will discuss what is Microsoft Exchange Server, Exchange Server roles, and Exchange Server architecture.
Table of Contents
Watch video
Watch this video on our YouTube channel and learn Exchange Server roles and architecture in depth.
What is Exchange Server
Microsoft Exchange Server is an email and calendaring server that runs on Windows server operating system. Exchange Server is also called a messaging platform. It provides flexibility for sending and receiving emails, calendaring, voicemail and scheduling meetings.
Features of Microsoft Exchange Server
Enhanced Security. Microsoft Exchange server is designed for optimal security and privacy with a variety of features at both the server and mailbox level. Microsoft Exchange Server uses Kerberos authentication (a network security protocol) that provides mutual authentication for a network connection. Additional security protocol support includes Secure Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (SMIME).
Calendars. Exchange Server includes rich features for personal, groups, and resource scheduling that integrates with e-mails, contacts, and tasks. Users can share their calendar information with other users, and they can view multiple calendars simultaneously.
Address Book. Contacts are stored in a centralized place that is called Address Book or Global Address List (GAL). We don’t need to worry about the email addresses of other users. All the addresses are automatically updated in the address book and they will come handy while composing new emails.
Enhanced Team Productivity. Microsoft Exchange Server maintains the communication between the users by providing them access to the services from the office and from home as well. Users can access their mailboxes, they can send and receive emails, or they can use other services either from office or home.
Mobility and Portability. Exchange server enables users to securely access email messages, instant messaging, voice mails, video calls and SMS texts from anywhere in the world. All they need is a computing device of their choice (laptop, desktop, tablet or mobile phones) and an internet connection.
Cloud Computing benefits. Exchange Server allows the users to move to the cloud. Be it immediate on-boarding to the cloud or managing a hybrid deployment with on-premises and online mailboxes to meet their business needs. It provides the end users a seamless experience that includes sharing multiple calendars and scheduling meetings between on-premises and online users.
High Availability and Site Resilience. Exchange Server is known for its High Availability (HA) features that ensure continued service in different outage scenarios. You can protect your Exchange Server mailbox databases and the data they contain by configuring your Exchange servers and databases for high availability and site resilience.
Functions of Exchange Server
Let’s understand what are the basic functions of Microsoft Exchange Server.
Mailbox Database: Every email server has a database where mailboxes, calendars, and recipients are stored.
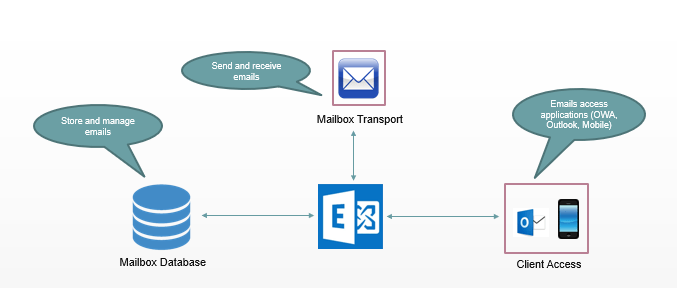
Client Access Services: Client Access is used by the email applications. For example, Outlook, OWA, and mobile clients. Users can use these applications to manage their emails and calendars.
Mailbox Transport Service: Mailbox Transport service is used to send and receive emails within the organization or outside the organization.
Edge Transport Server: To achieve higher level of security, Exchange server provides Edge Transport service. Edge Transport service is responsible to route inbound and outbound external emails.
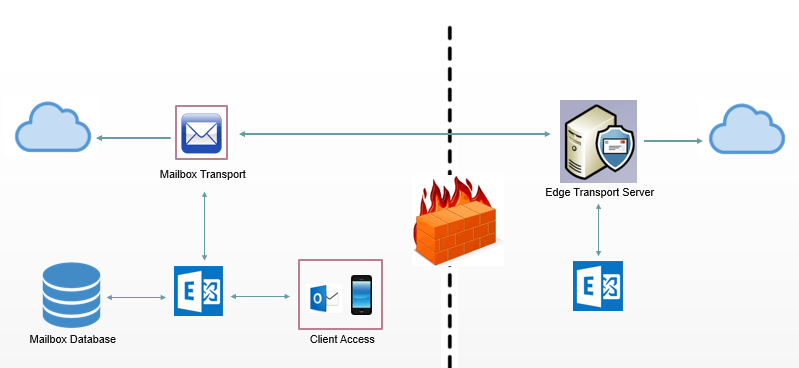
Edge Transport Server is always installed on the perimeter network. That means the Edge Transport Server uses a different network segment. It is always installed outside of the local network.
Exchange Server versions
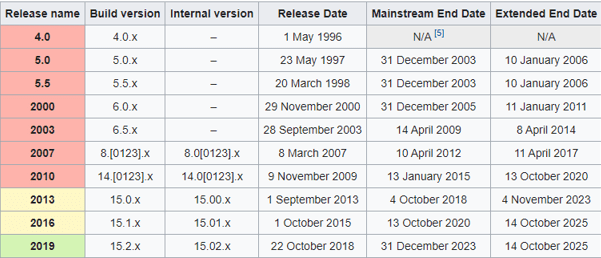
In below image you can see all the versions of Exchange Servers. The initial release for exchange server was Exchange Server 4.0 and the latest release is Exchange Server 2019. Since then a lot of changes are made within exchange server architecture.
Exchange Server roles
Exchange Server 2010 roles: In Exchange Server 2010, there are 5 roles. Mailbox Server, Client Access Server, Hub Transport Server, Edge Transport Server, and Unified Messaging Server.

- Mailbox Server: Mailbox Server role is the core role with in Exchange Server. It stores the mailboxes of the users and public folders. It hosts the mail enable objects such as contacts and distribution lists.
- Client Access Server: Client Access Server (CAS) role is responsible for serving client connections. For example, Outlook, OWA, Outlook Anywhere, Exchange Active Sync, EWS or Exchange Web Services, and POP and IMAP protocols.
- Hub Transport Server: Hub Transport Server handles the internal mail flow. This role is also responsible for applying transport rules and journaling policies to the emails those are going out from your organization. In addition, the Hub Transport Server delivers messages to the recipient mailboxes stored on the Mailbox Server.
- Edge Transport Server: Edge Transport Server role is a dedicated server function that performs spam and virus filtering as the first point of entry of the emails into an Exchange Server environment. It takes care of both inbound and outbound external emails routing. The Edge Transport server role should never be a member of your internal domain. It should be deployed on a perimeter network. We can install all the roles on the same server. For example, mailbox role or CAS role, or hub transport role but we cannot install Edge Transport role on the same server where other exchange server roles are installed. It has to be deployed on a separate server that is not connected to the local network.
- Unified Messaging Server: Unified Messaging Server role allows a user’s inbox to be used for voice messaging and fax capabilities. Exchange Server 2010 uses Unified Messaging Role as a capability of a voice mail server rather than having a separate voice mail system connected to the organization’s phone system.
Exchange Server 2013 roles: In Exchange Server 2013, 5 roles were consolidated in 3 roles. Mailbox Server, Client Access Server, and Edge Transport Server. Mailbox Server and Client Access Server roles can be installed on the same server. But again, Edge Transport Server will be installed on a different network.
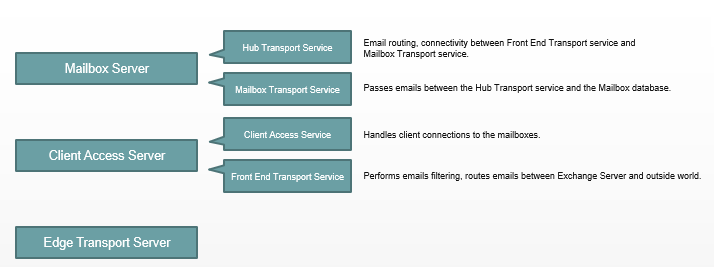
- Mailbox Server: In Exchange Server 2013, Mailbox Server role runs 2 transport services (Hub Transport Service and Mailbox Transport Service). Similar to the Exchange 2010 Hub Transport Server role, Hub Transport Service provides email routing within the organization and connectivity between the Front End Transport service and the Mailbox Transport service. Mailbox Transport Service passes emails between the Hub Transport service and the mailbox database.
- Client Access Server: Client Access server role is the server that handles requests from the clients. For example, Outlook, Outlook Web App and ActiveSync. Client Access server authenticates and redirects or proxies those requests to the appropriate Mailbox server. In Exchange Server 2013, Client Access Server has 2 main components. Client Access Service and Front End Transport Service. Client Access Service handles the client connections to the mailboxes. Front End Transport Service performs emails filtering and it handles the routing of emails between Exchange Server and the outside world.
- Edge Transport Server: Edge Transport Server is optional for organizations. It is designed to sit in a DMZ network to provide SMTP connectivity and the email flow in-and-out of the organization whether to the internet or Microsoft 365.
Exchange Server 2016 roles: In Exchange Server 2016, we have just 2 server roles. Mailbox Server, and Edge Transport Server.
Exchange Server 2019 roles: Like Exchange Server 2016, In Exchange Server 2019 we have 2 roles as well. Mailbox Server and Edge Transport Server. The Exchange Server 2019 mailbox server role includes multiple services and components that interact with each other and provides different messaging features. These services and component’s include client access services, transport services, and mailbox databases. So everything runs on mailbox server except the components of Edge Transport Server role that runs in perimeter network.
What is new in Exchange Server 2019
Now let’s understand what is new in Exchange Server 2019.
Improved search infrastructure: Exchange Server 2019 has a rebuilt search infrastructure for cloud scale and reliability in Exchange Online. This new search infrastructure allows for indexing of bigger files, simpler management, and better search performance.
Unified Messaging removed: With Exchange 2019, Microsoft says goodbye to the Unified Messaging role. Now you must be thinking, what happens with voicemail if you are migrating from Exchange 2016 to Exchange 2019? So all Unified Messaging enabled mailboxes will be disabled. There will be no voice mail or auto-attendant processing or any Unified Messaging settings available in Outlook, Outlook on the web, or in Exchange Control Panel. But the good news is that the existing voicemail will remain in form of attachments.
Security-focused Exchange released: Each and every Exchange version was announced to be more secure than the previous one. Even before the official release of Exchange 2019, it was mentioned that Exchange 2019 has been created with Windows Server Core version in mind. And the most important reason for this decision is security. The advantages of the Server Core edition are, that it has smaller footprint, greatly reduced attack surface, and less features those are not crucial for the email server. Installing Exchange on the Server Core version does not mean that you will need to switch to using PowerShell for all your admin related tasks. All Microsoft Management Console (MMC) tools, like Hybrid Configuration Wizard, Event Viewer or EAC can be used remotely.
Client Access rules: In Exchange Server 2019, you can allow or restrict access to Exchange Admin Center and to PowerShell. The criteria can base on IP Address, authentication type, and user property values. With the help of these rules, it is possible to ensure that there are no unauthorized connections to your Exchange environment. And you can even allow certain users to use PowerShell for specific time frames.
Conclusion
In this blog we learnt what is Microsoft Exchange Server, Exchange Server architecture and its features, we learnt what are the functions of Exchange Server, and the different types roles in Exchange Server.
Found this article helpful and informative? You may also like Microsoft 365 Tenant to Tenant Migration. Don’t forget to follow us and share this article.
Related articles
We welcome you to browse our other articles on Exchange Server 2019 and Exchange Hybrid deployment:
DNS records in Active Directory
Install Active Directory on Windows Server 2019 and promote to Domain Controller
40+ Exchange Hybrid Interview questions and answers
Exchange Hybrid Free/Busy. Troubleshoot Free/Busy in Exchange Hybrid
What is Exchange Hybrid deployment
Demystifying Autodiscover. A Deep Dive into Autodiscover.
Happy Learning!!
