What is an Email Header and how to analyze Email Headers
In this “How to analyze email header” guide, we break down the process step-by-step, showing you how to read email header to uncover valuable information about the sender, the route the email took, and potential security risks. In this blog we will learn what is an Email Header, we will discuss how to view email header in Outlook and OWA, we will discuss what is P1 and P2 header, and we will learn how to analyze email header.
Table of Contents
Watch the video
Watch this video and learn how to read email headers.
What is an Email Header
Before we discuss what is an email header, let’s discuss how a letter or an envelope is sent to the recipients. In the below example, John is sending a letter to Bob.
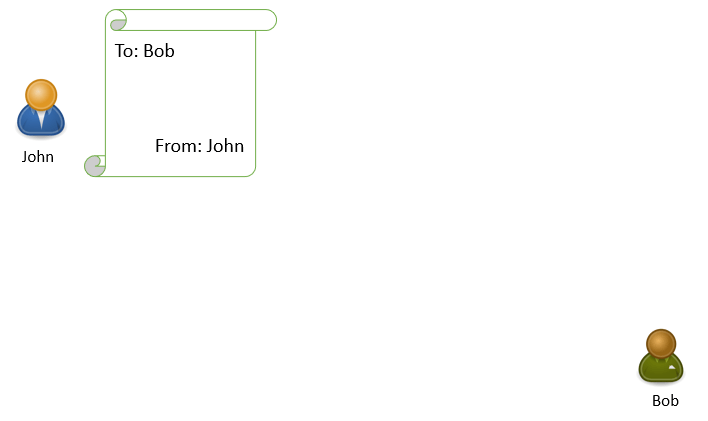
John will write a letter, he will type the name and address of Bob in the TO field, and in FROM field he will type his name and address.
When John will send this letter, a postman will pick this letter and will check TO and FROM details.
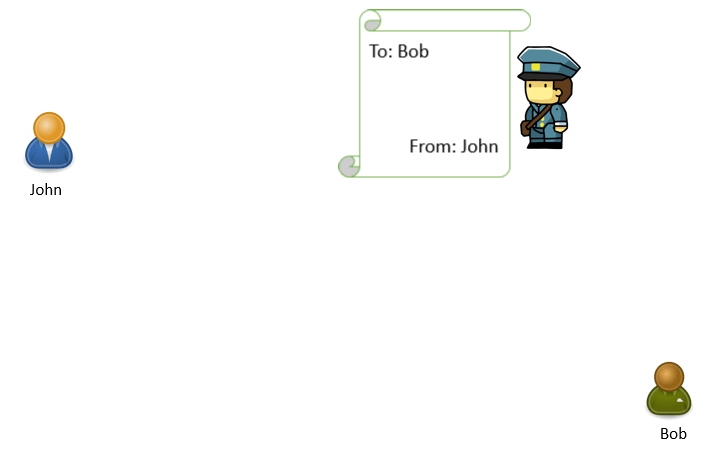
The address written in the TO field is the address of the recipient where this postman will deliver this letter, and FROM address will be treated as return-path to return this letter in case Bob’s address is not found. If postman is able to find the recipient address, he will deliver this letter to Bob. And if he doesn’t find the address, he will return this letter to the address which is mentioned in FROM field (John’s address).
P1 vs P2 Header
An email header is divided in P1 header and P2 header.
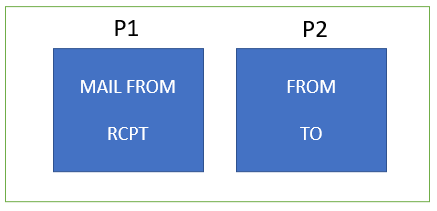
P1 header includes MAIL FROM and RCPT, and P2 header includes FROM and TO. In email headers, P1 and P2 headers are like labels on a package. They help email systems understand where the email came from and where it’s going. These headers contain important details about the sender, recipient, and the path the email traveled. Think of them as the addresses and stamps on an envelope that help it reach its destination accurately.
If we compare MAIL FROM and FROM attributes, these look same. But in case of an email header, MAIL FROM is a return-path address where NDR or bounce-back messages will be sent, and FROM attribute is the email address from where an email was sent.
Important: In few scenarios Return-path and FROM addresses will differ. For example when an application is sending emails on your behalf. P2 header (FROM and TO) are the values that a user see in his Outlook or OWA.
How to view Email Header in Outlook and OWA
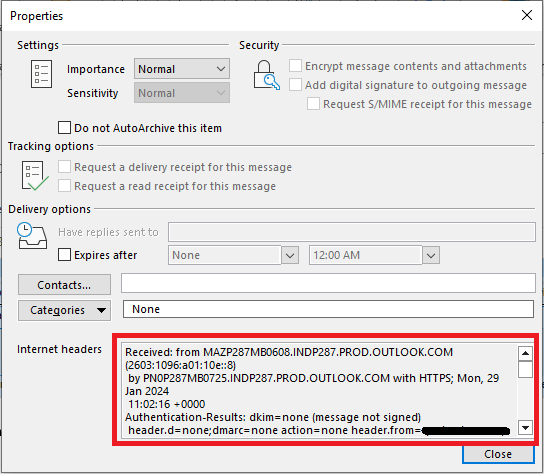
To view email header in Outlook, double click the email, go to File and click Properties, and copy the text under Internet headers as shown below.
To view email header in OWA, select the email, click 3 dots as shown below.
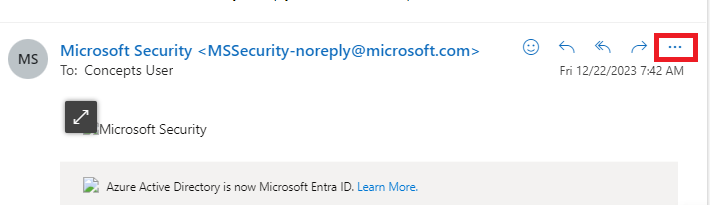
Click View, click View message details and copy the text under Message details.

How to analyze Email Header
After copying email header text either from Outlook or OWA as shown above, go to email header analyzer and paste the copied text and then click Analyze headers.
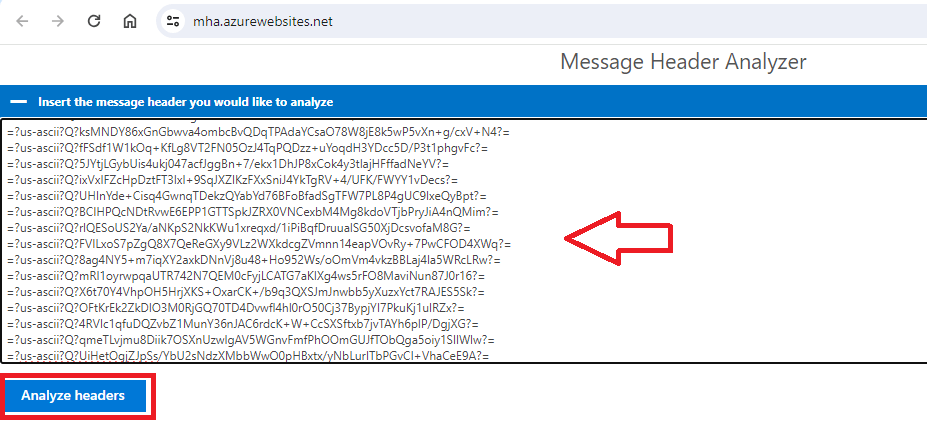
If we analyze an email header, the first section will give a summary of the email.
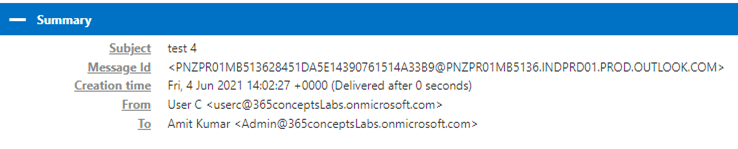
In the Summary section of an email header we will find below information:
Subject of the email.
Message Id is a unique ID assigned to the email. With the help of a message ID, we can track the routing of a particular email. Message ID is assigned by the email server that processes the email.
Creation Time has the date and time when this email was sent by the sender.
FROM address contains the email address of the sender.
TO address contains the email address of the recipient.
The next section in an email header is Received Headers.
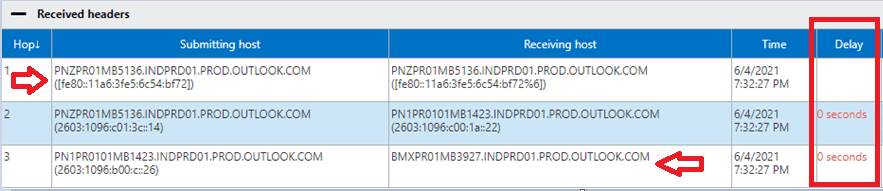
Under Received Headers section of an email header we can see the routing of the email. We can see from which server this email was sent, which server processed this email, and to which server this email was delivered. In this section we can also see if there was a delay in the delivery of this email.
Next section in an email header is Forefront Antispam Report Header.
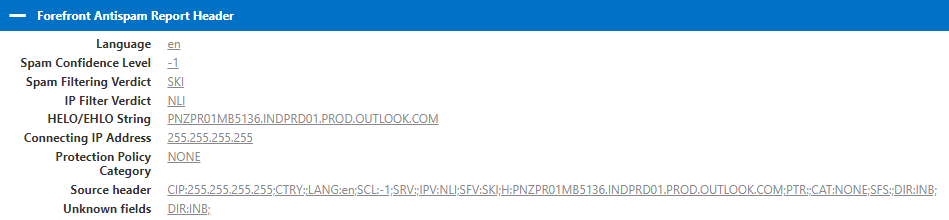
Under Forefront Antispam Report Header section we can find below information:
- Language indicates in what language this email was sent by the sender.
- SPAM confidence level is a value which is stamped on an email as per the action taken by the anti-spam filtering within Exchange Online Protection. If SCL is -1 that means this email is an internal email or Spam filtering was by passed on that email. If SCL value is 0 to 1, that means this particular email is not a SPAM email. If SCL value ranges from 5 to 6, in that case this email is a spam email. And if SCL value is 9, that means this particular email is filtered as High confidence SPAM.
- Spam Filtering Verdict is a value which is stamped by the anti-spam filtering policies during filtering of the emails. Spam filtering verdict depends on the SCL value which is assigned to a particular email. In this example Spam filtering verdict is SKI, that means spam filtering was skipped on this email because this is an internal email. If email is categorized as SPAM, then spam filtering verdict will be SPM. If email is not spam, then verdict will be NSPM.
- IP Filter Verdict indicates if the sender’s IP address has a good reputation or it is listed on the Internet. NLI means this IP address was not found on any IP reputation list.
- HELO/EHLO String stands for Helo or Extended Helo string. This attribute has a name of the server which has processed this particular email. This is known as connecting server as well.
- Connecting IP Address is the IP address of the email server that has processed this email post it was sent from the sender’s application.
- Protection Policy will show the category that was applied on a particular email. If category is blank, that means this email was sent to an internal user. If email was marked as SPAM, category for that email will be SPM. There are few categories which can be applied to the emails as per the SCL values. For example, BULK, PHISH (phishing emails), OSPM (outbound spam), and MALW (malware).
- Source header will give you a consolidated view where we can check connecting IP address, SCL value, IP filter verdict, language, and the country from where the email was sent.
- Unknown Fields will show if email is an inbound email or this is an outbound email.
In the next section of the email header we will see authentication results.
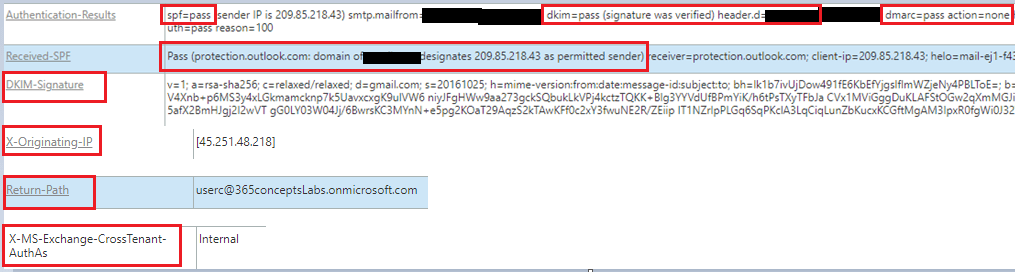
- Under Authentication-Results we can see whether SPF was pass or failed on this email, we can check the IP address of the sender, we can see from which domain the email was sent, we can see if DKIM was passed or it got failed on this email, we can check which domain added the DKIM digital signatures on this email, we can check if DMARC was passed or it got failed on this email, and what action was taken by the recipient email server as per the policy defined by the sender’s domain in DMARC record.
- Received SPF shows the details of the SPF results. Under this tab we can find details of SPF validation. We can check if the sender’s IP address was added within his SPF record or not.
- DKIM signatures shows the signatures which were stamped by the sender’s email server.
- X-Originating-IP is the public IP address that the sender used to send this email. Most of the time this attribute will show you a public IP address of your ISP. Return-Path is the email address to which a bounce-back or an NDR will be sent in case email is not delivered to the recipient.
- X-MS-Exchange-CrossTenant-AuthAs shows if email is an internal email or external email. If email is an internal email you will see a value Internal. If this is an external email the value will be Anonymous.
Conclusion
In this blog we learnt what is an email header, we learnt what is the difference between P1 header and P2 header, we talked about how to view email header in Outlook and OWA, and how to analyze email header.
You might like our other articles on Troubleshoot Exchange Online Mail Flow and Exchange Online Mail Flow Interview Q&A,
If you found this blog helpful, please share it within your community and do not forget to share your feedback in the comments below. Please join our YouTube channel for the latest videos on the Cloud technology and join our Newsletter for the early access of the blogs and updates.
Happy Learning!!
