50+ Microsoft Exchange Online interview questions and answers
Exchange Online is a cloud-based email and calendaring service provided by Microsoft as part of their Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365) suite of productivity tools. It is a hosted version of Microsoft Exchange Server, which is a popular email server and collaboration platform used by businesses and organizations worldwide.
If you are preparing yourself for an interview and your job responsibilities will be to deal with Exchange Online administration, this is the right place to start with. These top 50+ Exchange Online interview questions and answers will help you to prepare yourself for the technical round.
Before you go through these Microsoft Exchange Online interview questions and answers, we recommend you to go through our YouTube channel Office365Concepts first and get a good understanding of Exchange Online topics.
We have categorized these Microsoft Exchange Online interview questions and answers in different levels:
Freshers
Intermediate Level
Experienced
Top 10 frequently asked Microsoft Exchange Online interview questions and answers for freshers.
- What is Office 365?
- What is a security group?
- What is the difference between a distribution group and dynamic-distribution group?
- Which DNS record is used to verify a domain in Office 365 tenant?
- What DNS record is used for autodiscover in Exchange?
- What is the value of CNAME record in Office 365?
- What is Exchange Online as per your understanding?
- Which Exchange Online license you would suggest if I want to provision a mailbox?
- Scenario: I am not able to configure my mailbox in Outlook desktop client, what will be your course of action?
- What is the difference between Global Admin and Global Reader role?
Microsoft Exchange Online interview questions and answers for freshers
1. What is Office 365?
Office 365 is cloud-based subscription model. (Now the next question can be “what do you mean by a subscription model ?”). A subscription model is where you need to purchase a license/subscription to use certain services. On top of this you can also add Office 365 is also called SaaS (Software as a Service). Note: But make sure you know what is SaaS.
To know more about “What is Office 365” refer to this video.
2. What is a security group?
A security group is used to assign bulk permissions to the users or devices.
To learn more about security groups, refer to this video.
3. What is the difference between a distribution group and dynamic-distribution group?
Both distribution group and dynamic-distribution group are used to distribute emails. The difference between two is how we add members within these groups. In distribution group, we add members manually, whereas in dynamic-distribution group, we add users basis on conditions. For example, if a user is part of HR department, or a user’s city attribute is set to Delhi.
To understand working of groups, refer to this video.
4. Which DNS record is used to verify a domain in Office 365 tenant?
We use either TXT or MX record to verify a domain in Office 365 tenant.
To learn more about DNS records, refer to this video.
5. What DNS record is used for autodiscover in Exchange?
CNAME record.
6. What is the value of CNAME record in Office 365?
domain.autodiscover.com = autodiscover.outlook.com
7. What is Exchange Online as per your understanding?
Exchange Online is a cloud-based messaging platform that provides access to features like calendar, emails, address book, contacts, and tasks. Once you have supported Exchange Online license, you can access your emails and calendar through Outlook desktop client, mobile app, or from OWA (Outlook on the Web).
8. Which Exchange Online license you would suggest if I want to provision a mailbox?
Here, you can name any license that provides access to a mailbox. For example, Exchange Online Plan 1, Plan 2, Microsoft Business Standard or Microsoft Business Premium.
9. Scenario: I am not able to configure my mailbox in Outlook desktop client, what will be your course of action?
First ask “what error you are getting while configuring profile in Outlook client ? Never jump directly to the troubleshooting part”. Since you are applying for L1 role, you can tell few basic steps for troubleshooting. You can use SaRA tool to troubleshoot outlook profile issue, If you are getting password incorrect issue, delete cached credentials from credential manager, reset your password and try again, and so on.
10. What is the difference between Global Admin and Global Reader role?
A Global Admin can do all the tasks within all Microsoft Online services. Where as a Global Reader has view only permission. They can see all the admin features but they cannot edit any settings.
11. What is a shared mailbox?
A shared mailbox is used for collaboration. Multiple users can have permission on the shared mailbox and they can add it to their Outlook client or in OWA.
To know more about shared mailbox, refer to this video.
12. If I want to add a shared mailbox or a user mailbox in my outlook or OWA as a secondary mailbox, which permission I would require ?
Full Access permission.
13. If I delete an email from my Inbox, for how many days that email will be stored in Deleted Items folder?
30 Days.
14. How many types of Retention Tags are available in Exchange Online?
3 Tags. Default Policy Tag (DPT), Retention Policy Tag (RPT), Personal Tag.
To learn Exchange Retention Policies and Retention Tags, refer to this video.
Microsoft Exchange Online interview questions and answers for intermediate level
15. If a user of my tenant lost his emails, can i recover them as an administrator?
Yes, you can run e-Discovery or Content Search to recover those emails.
To learn more about content search, refer to this video.
16. What is Litigation Hold?
Litigation hold is used to place mailbox contents on hold. If a user deletes emails from the mailbox that has litigation hold enabled, those emails are preserved within mailbox folder, and later an Administrator can recover them.
Now the interviewer can ask in which folder these emails are preserved. So the answer will be Purges folder.
17. Scenario: All of the users of my Office 365 tenant are not able to receive external emails but they can receive internal emails. What could be the issue?
You need to verify if MX record is published for your Office 365 domain since all users are not able to receive any external email. You can use mxtoolbox.com to verify your DNS record.
18. How would you find if an email is a spam email?
Collect email header and look for SCL value in email header. If SCL is equal or greater than 5, that email is a spam email.
19. What does SCL-1 mean?
SCL-1 indicates an email is marked as internal email or spam filtering is skipped on that email.
20. What does NSPM mean in Exchange email header?
NSPM indicates the email in question is not a spam email.
21. What is autodiscover?
Autodiscover is a service of Exchange that automatically configures outlook profile without requiring server details. You will enter your username and password while configuring profile in outlook, and outlook will automatically configure your profile.
22. What is Azure Active Directory?
Azure Active Directory is a cloud-based active directory for Microsoft Online services that authenticates and authorizes the users.
To get an understanding of Azure Active Directory and its features, refer to this video. You can also refer to this article.
23. Being an Administrator if I want to check how many emails a user has sent today, where I can check this report?
You can run Message Trace by adding the user in Sender field and run message trace report for 24 hours.
24. What is maximum size of a shared mailbox? Can we increase storage space of a shared mailbox?
Shared mailbox’s default storage space is 50 GB. If you want to increase this space, you need to assign Exchange Online Plan 2 (Exchange Online Plan 2 provides 100GB storage space) license to the shared mailbox account.
25. Which PowerShell command is used to get a list of all mailboxes in my tenant?
Get-Mailbox. If you have more than 1000 mailboxes in your tenant then you need to use -Resultsize Unlimited switch along with this command. For example, Get-Mailbox -Resultsize Unlimited.
26. Why do we use Set command in PowerShell, like Set-Mailbox or Set-User?
Set command is used to modify the properties of a user or the mailbox.
27. Scenario: I want to import 100 PST files into mailboxes of my Office 365 tenant, which option would you suggest me?
Do not suggest to import PST file from Outlook client because admin has to import 100 PST files and doing it one by one is not feasible at all. You can use Network Upload in Office 365 to bulk import PST files.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/compliance/use-network-upload-to-import-pst-files?view=o365-worldwide
28. What is Global Address List (GAL)?
GAL is a directory in Exchange Online (it is available in on-premise Exchange Server as well) where all the recipients are added. If you want to send email to someone within your organization, you can find that user within GAL.
29. What is Online Archive?
Online Archive is a storage space that is allocated to a mailbox and users can move their emails to online archive. This storage space does not consume the actual mailbox storage space.
30. From where you can manage mail flow in Office 365?
From Exchange Admin Center.
Microsoft Exchange Online interview questions and answers for experienced
31. Explain Exchange Online Protection architecture (EOP)?
Exchange Online Protection (EOP) has multiple filtering servers that filter emails. (when these are coming to your organization or going out of the organization).
Exchange Online Protection has multiple filters that scan emails. Connection Filter, Anti-Malware Filter, Transport Rule and DLP, ATP (Advanced Threat Protection), Anti-Spam/Content Filter, Zero-hour Auto Purge (ZAP). (This is the order of filtering servers in EOP).
Connection Filter: Connection Filter checks the IP address from where an email sent. It checks its reputation using pre-built Reputation List. Mailbox level safe sender list is triggered on Connection Filter, and DBEB also triggers on Connection filter.
Anti-Malware Filter: This filter scans the email attachments and its body for malicious contents. If any malicious contents are found, email is sent to Quarantine and only an Administrator can release that email.
Transport Rule & DLP: On this stage email is scanned against Transport Rules (if created any), and if DLP (Data Loss Prevention policy) is enabled in tenant, these rules are triggered on email when it is sent out from the organization.
ATP: If ATP is enabled in tenant, Safe Attachment scans the emails for viruses and take action as per the policy configuration. And Safe URL scans URLs within the email and blocks or re-writes those URLs as per the configuration done within the policy. To learn more about ATP, refer to this video.
Anti-Spam or Content Filter: Anti-Spam filter scans the emails against SPAM, PHISH, HPHISH, BULK, or SPOOF, and takes action on the email as per the action specified within the policy.
ZAP (Zero-Hour Auto Purge): ZAP is a feature of ATP. It scans the emails when the email is reached the mailbox.
For a deep-dive session on EOP, refer to this video.
32. How does SPF record work?
SPF is used to validate if the email is sent by a legitimate sender. A sender will add their email server’s IP address or the Full Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) in SPF record on his domain provider, when recipient email server will receive the email, it will check the FROM header and will extract the domain name from the FROM header.
With the help of domain name (extracted from FROM header) recipient email server will go to public DNS, it will check the SPF record and will validate if the IP address or the FQDN from which the email was sent, is added within the SPF record or not. If it is added, SPF record will pass, if it is not added, in that case SPF record will fail, and as per the action specified within SPAM Filter policy at recipient side, action will be taken on that email.
To learn more about SPF record, refer to this video.
33. What values you can find under X-Forefront-AntiSpam-Report header in an email header?
This section includes information about Spam confidence level (SCL), Spam filtering verdict (SFV), Connecting IP address, and IPV information.
Refer to this video if you want to learn how to analyze email header.
34. With the help of an email header, how would you find if ATP has taken action on the email or not?
If you see below values in email header, that means ATP was triggered on that email:
X-MS-Exchange-Organization-SafeAttachmentProcessing
X-MS-Exchange-Organization-SafeLinksProcessing
35. Where does SPF record work in EOP architecture?
SPF works in Anti-Spam/Content filtering.
36. Where does DBEB work in EOP architecture?
DBEB work on Connection Filter in EOP.
37. How does DKIM work?
DKIM is an email security standard which is designed to make sure the emails are not altered during the transmission from source to destination. As soon as you send an email DKIM uses public-key cryptography to sign that email with a private key.
38. How does recipient email server validates email that is signed by DKIM?
Recipient email server checks d=domain.com value in email header, with the help of domain name recipient email server reaches to public DNS and finds the CNAME record. These CNAME records are used as a public key by the recipient email servers, to verify if the email’s body hasn’t changed during the transmission. Once the signatures are verified by the recipient email server, DKIM will pas, and the email is treated as authentic email.
To learn how DKIM work, refer to this video.
39. What is DMARC record and how does it work?
DMARC helps the recipient email servers to determine what action they should take on your emails if SPF or DKIM checks fail. DMARC works with SPF and DKIM. Before you enable DMARC, you need to add SPF and DKIM records for your domain.
When an email is received, recipient server extracts the domain name from the return-path in email header.
Then Recipient server extracts domain Name from FROM address within email header, and matches both Domain names. This is called SPF alignment.
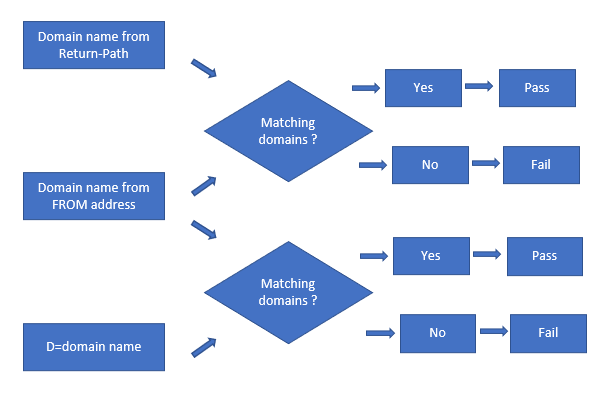
If both domain names are matching, SPF will pass. If domain names are not matching, SPF will fail. And if SPF alignment fails, recipient server will now check DKIM validation.
Recipient server will check the domain name within “D=” attribute, and will match that domain with the domain name extracted from the FROM address. “D=” is a value that is found within the DKIM signatures, which indicates which domain has signed this particular email.
If both domain names match, DKIM will pass. Else DKIM will fail.
Now, if either SPF or DKIM check fails, recipient server will treat that email as per the action specified by the sending server within the DMARC record.
To learn more about DMARC, refer to this video
40. One of my users is receiving duplicate email. How would you troubleshoot this issue?
In this scenario, most of the time culprit is active sync device. To isolate the issue we can disable Active Sync protocol for the user and ask him to monitor the behavior.
41. I want to stop display name spoofing for one of my users in my Office 365 tenant. What options would you recommend me?
You can create either a transport rule to stop display name spoofing or you can use Impersonation in Anti-Phishing policies in EOP.
42. I want to find out if there was a delay in email delivery. How can i check this?
There are 2 ways to check email delivery delay. You can collect email header and look for hops. This will show the time taken by email to travel from one hop to another.
Second way is Extended Message Trace. In EMT you can look for Latency field. This will show the delay if there was any.
43. What does IPV:NLI mean in EOP?
IPV:NLI means the IP address from where we received email, this IP was not listed in any reputation list. This value is stamped by Connection Filter policy in EOP.
44. If I want to route all emails from my Office 365 tenant to a 3rd party email filtering service, what type of connector I need to create in EOP?
Office 365 to Partner Organization.
45. How would you find if an email is a spoof email?
Collect email header and look for FROM address and Return-Path. If both have different values, that means this email is a spoof email.
46. What is Connecting IP in email header?
Connecting IP is the IP address of the sender email server that has processed the email.
47. What is conditional email routing in Exchange Online?
In some scenarios we might have to route our emails to a different mail server, in that case we create connector in EOP and route all emails to that email server. This is called conditional email routing.
48. What is Sandbox in ATP ?
Sandbox in ATP is a virtual environment where attachments are scanned. When an attachment enters the sandbox environment, a detonation chamber analyses the attachment and determines whether this attachment is safe or not.
To learn more about Sandbox and ATP, refer to this video
49. What is Zero-hour auto purge?
Zero-hour auto purge (ZAP) is email protection feature that detects and neutralizes the malicious contents (phishing, spam or malware) that have been already delivered to the mailboxes.
50. How would you find if ZAP is triggered on an email?
Collect email header and look for X-Microsoft-Antispam-ZAP-Message-Info
51. What does Generating Server mean in NDR (bounce back message)?
Generating Server field will show the name of the server that has generated the NDR.
52. Scenario: All of the emails sent from my tenant to all the external domains are marked as SPAM by the recipient email servers. What could be the issue?
Collect email header from one of the recipients, check if Connecting IP is listed in internet. If yes, de-list it and then check behavior.
Or, issue could be because of HRDP. Collect email header from recipient and look for SFP:1501 value in email header. This indicates the emails are being routed through HRDP (low reputation IP addresses).
53. Scenario: I am using Exchange Online Protection (EOP) and MX record for my domain is pointed to a 3rd party email filter solution. An external sender is sending me an email but I am not receiving it. What would be your course of action?
Run message trace at recipient side, if we see that email in message trace, this will show if email was delivered to the inbox folder, it was delivered to the junk folder or it was forwarded. If there is no email in message trace, in that case we need to check if email was received by 3rd party email filtering server because MX record is pointed to that server.
If email is delivered at 3rd party email filtering server, then the issue could be with the settings on that server or the connector created between the server and EOP.
54. Scenario: One of the external senders is sending me an email but I am not receiving that email and the sender is not getting any NDR. What would be your course of action?
If sender is not getting NDR while sending email and that email is not reflecting in message trace in your tenant, then ask sender to send that email from another email application.
55. What does SCL-1 mean in email header?
SCL-1 indicates the email is marked as internal or Spam Filtering was skipped on that email.
After going through Microsoft Exchange Online interview questions and answers we welcome you to go through below interview and questions on other cloud technologies.
Top 50+ Office 365 interview questions and answers
40+ Exchange Hybrid interview questions and answers
Good Luck!
