How does SPF work (Sender Policy Framework)
In this article we will learn what is SPF record (Sender Policy Framework), why do you need SPF record for your domain, we will discuss how SPF record works, how to create SPF record and how to verify SPF record.
Table of Contents
Watch the video
Watch this video and learn all the important concepts of SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record.
What is SPF record?
If we go by definition, SPF (Sender Policy Framework) record helps an organization from receiving Spoof or Phishing emails. SPF record determines whether or not a sender is permitted to send emails on behalf of a domain. If the sender isn’t permitted to do so, SPF check will fail for that email on the receiving server and the spam policy configured on the receiving server determines what to do with the message.
Why do you need SPF record for your domain
let’s assume we have 2 different organizations abc.com and xyz.com. One of the users from abc.com organization, bob@abc.com wants to send an email to a user john@xyz.com in xyz.com organization.
Bob will compose an email and will type the email address of john, and will send that email from his email application.
This email will be processed by one of the email servers within abc.com organization, and during that process few attributes will be added within the email header of the email as shown below. For example, connecting IP address, FROM address, TO address, and Return-Path. Where Connecting IP address will be the IP address of the sender’s email server which is processing that email, and Return-Path is the email address to which an NDR or bounce-back message will be sent in case the email is not delivered.
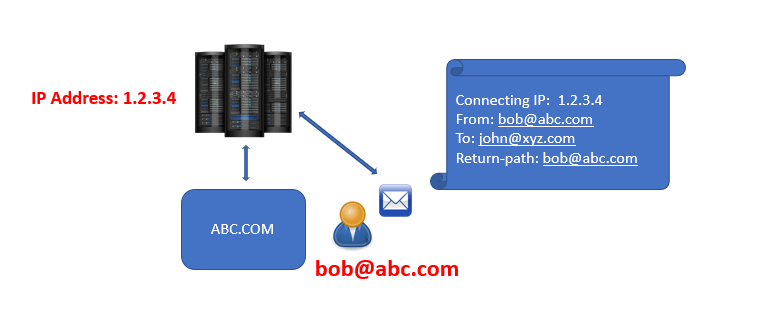
When Bob will send this email to John, it will be received by an email server of xyz.com organization. The recipient email server will analyze the email and will check if this is a legitimate email or not.
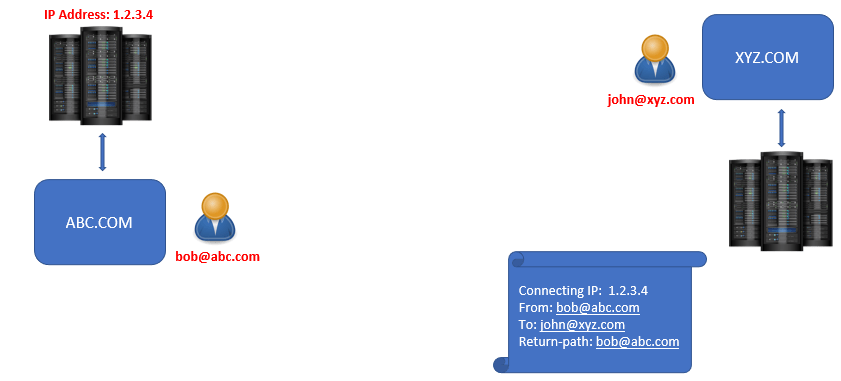
But the question arises, how recipient email server will trust if the sender of this email is the actual owner of abc.com domain, or how this server will verify if the IP address 1.2.3.4 is the IP address of the sender’s email server?
Let’s consider one more example. Let’s assume we have 2 organizations abc.com and xyz.com. Let’s say, someone who doesn’t belong to abc.com or xyz.com organization, is trying to send an email to John using Bob’s email address.
But this time, this email will not be processed by the email server of abc.com because the email is not sent from their network. So this email will be processed by a random email server and during that process few attributes will be added within the email header as shown below:
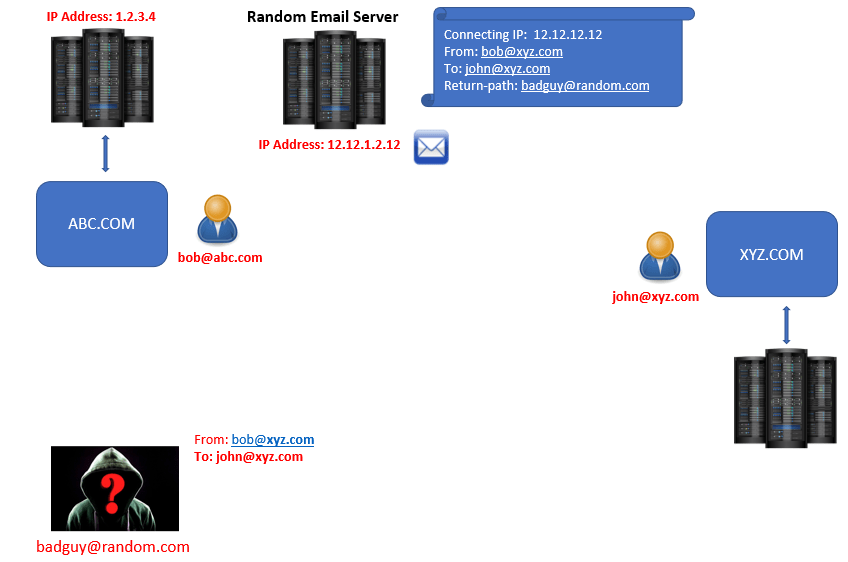
Now guess what, this time connecting IP address will be the IP address of the email server that has processed this email that is 12.12.12.12. FROM address will be the email address of bob@abc.com because his email address was used to send this email. And TO field will contain the email address of john@xyz.com. But the return-path will not be the same as the FROM address. Return-path will have the email address badguy@random.com. This is called Spoof email.
Now this email will be sent to the recipient email server and it will run few checks on this email to identity if this email is a legitimate email or not.
But how recipient email server will identity if this is a Spoof email, or whether this email was actually sent by bob@abc.com, or the IP address 12.12.12.12 belongs to abc.com organization. And the answer is SPF record.
How SPF record works?
Now let’s understand how SPF record works and does SPF record help the recipient email servers to identify if the email is a legitimate email or it is sent by somebody who doesn’t belong to that domain.
Let’s assume abc.com organization has now added an SPF record for their domain in public DNS and the IP address 1.2.3.4 of their email server is added within the SPF record.
Bob@xyz.com is sending another email to john@abc.com. When this email will be sent and when it will be processed by abc.com email server, few attributes will be added within the email header. For example, Connecting IP address, FROM address, TO address, and Return-Path.
When recipient email server will receive this email, it will check the Return-Path within the email header, and will extract the domain name from Return-Path.
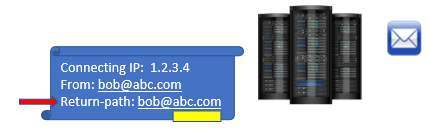
As of now, the recipient email server knows that this email was sent from abc.com domain. But, what if the connecting IP belongs to abc.com domain or not. To verify this, the recipient email server will reach the public DNS of abc.com domain (with the help of domain name extracted from FROM address) and will ask public DNS for the SPF record for abc.com domain.
Public DNS will return the SPF record details for abc.com domain to the recipient server, and recipient email server will check if the connecting IP address is added within the SPF record or not.
If the sending email server’s IP address will be found within the SPF record, SPF check will pass and the email will be delivered to john@xyz.com. But if sending email server’s IP address is not found within the SPF record, SPF check will fail and the recipient email server will treat this email as per the action specified within the SPAM filtering policies.
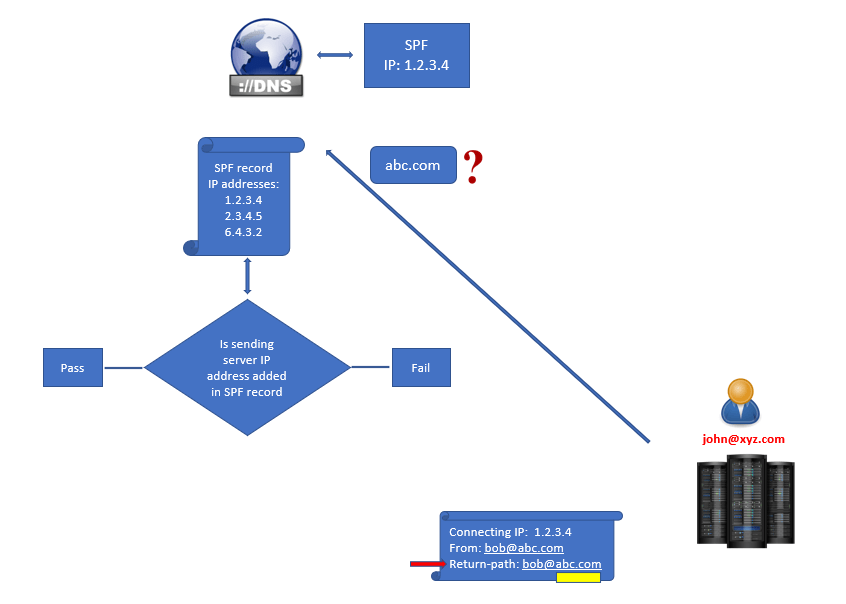
So this is how SPF record works.
How to create SPF record
A typical SPF record for Office 365 domain looks like below:
v=spf1 include:spf.protection.outlook.com –allSPF record has 3 components: Version, SPF value, and Enforcement Rule.
Version: Version specifies the version of SPF record. An SPF record will always start with v=spf1.
SPF Value: Value defines the IP address or the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the email server for which you are adding the SPF record. In the above example, spf.protection.outlook.com indicates that the domain for which you are adding SPF record is added in Office 365. If you want to add an IP address in SPF record, then value will be as below:
v=spf1 ip4:192.168.0.1 include:spf.protection.outlook.com -allIn the above example of SPF record, 192.168.0.1 is the IP address of your email server or an application from where you are sending emails, and spf.protection.outlook.com indicates that the domain for which you are adding this SPF record that domain is verified in Office 365 Tenant, and you will be sending emails from this domain as well.
Enforcement Rule: Enforcement rule is of 3 types: Hard Fail, Soft Fail, and Neutral.
Hard Fail: Hard Fail enforcement rule indicates that I have only one server from where i will be sending the emails and that server FQDN or IP Address is added within the SPF record.
Soft Fail: Soft Fail is used when we are not sure how many email servers we have in our organization. That means my users can send emails from any server and I haven’t added all the servers within the SPF record.
Neutral: Neutral is reserved for testing purposes. This type of enforcement rule is not used in the production environment.
How to verify SPF record
SPF is a TXT record that is added in public DNS portal. Once you have added a TXT SPF record for your domain in public DNS, you can verify SPF record in 2 ways.
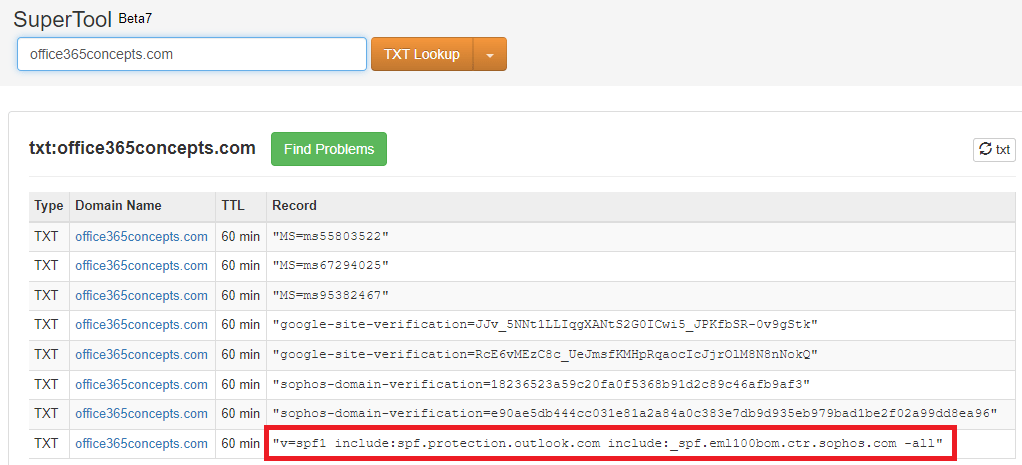
Go to MXToolbox and type txt:domain.com and press Enter. This will show if you have added SPF record for your domain and whether this record is published on the Internet. In the below image you can see the SPF record for office365concepts.com domain.
The other way to verify SPF record or any other DNS record is NSLOOKUP. Open Command Prompt and run below commands one by one:
NSLOOKUP
Set q=txt
yourdomain.com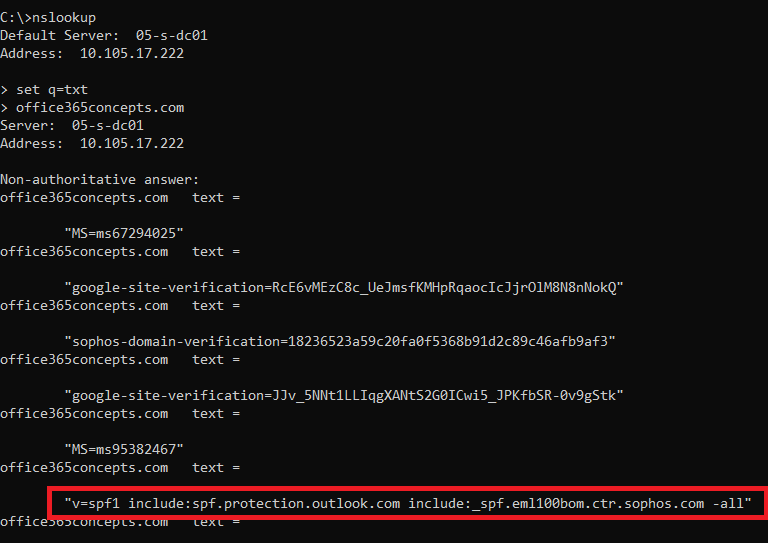
How to troubleshoot SPF record
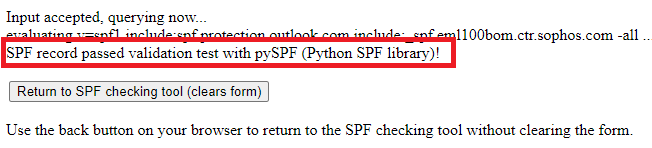
To troubleshoot SPF record, use this tool. Go to Check SPF record section and type your domain name and the SPF record value (without quotes) as shown below and click Check SPF Record.
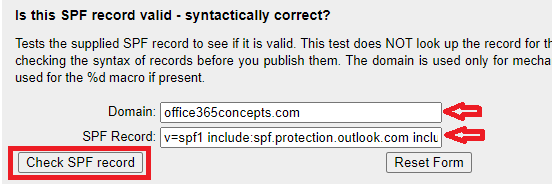
This tool will analyze the SPF record against your domain, it will check the syntax of the SPF record and will show the results.
Conclusion
- SPF is a TXT record which is added within the public DNS of a particular domain.
- SPF record helps an organization from receiving Spoof or Phishing emails. SPF record validates the sending email server by verifying the IP address of the sender against the owner of the domain.
- SPF record Increases domain reputation by stopping domain impersonation and email spoofing.
- SPF record is used to ensure that the recipient or destination email server trust the messages those are sent from your organization.
If you found this article helpful and informative, please share it within your community and do not forget to share your feedback in the comments below.
You might like our free courses on ADFS, Exchange Server 2019, and Exchange Hybrid Deployment.
Please join us on our YouTube channel for the latest videos on Cloud technology and join our Newsletter for the early access of the blogs and updates.
Happy Learning!!
