What is DMARC record
In this blog you will learn what is DMARC record, how DMARC record works, and you will learn how to create a DMARC record.
Table of Contents
Watch the video
Watch this video and learn how DMARC record works, and what is the background process of DMARC record.
What is DMARC record
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) record helps the recipient email servers to determine what action they should take on the emails if SPF or DKIM checks fail. DMARC record works with SPF and DKIM. Before you enable DMARC record for your domain, you must need SPF and DKIM records published for that domain.
DMARC record ensures the destination email systems trust messages sent from your domain. Using DMARC with SPF and DKIM gives organizations more protection against spoofing and phishing email. DMARC helps receiving mail systems decide what to do with the messages from your domain that fail SPF or DKIM checks.
How DMARC works
Let’s consider one example to understand how DMARC works. Let’s assume we have 2 organizations ABC.COM and XYZ.COM. ABC.COM organization has published SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records in their public DNS.
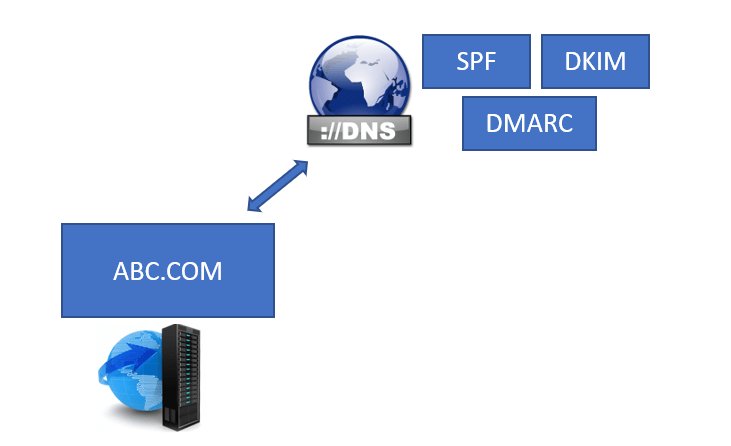
In this example, ABC.COM is going to send an email to XYZ.COM organization. When this email will be sent to XYZ.COM organization, their email server will perform few checks to validate if the email is a legitimate email or not.
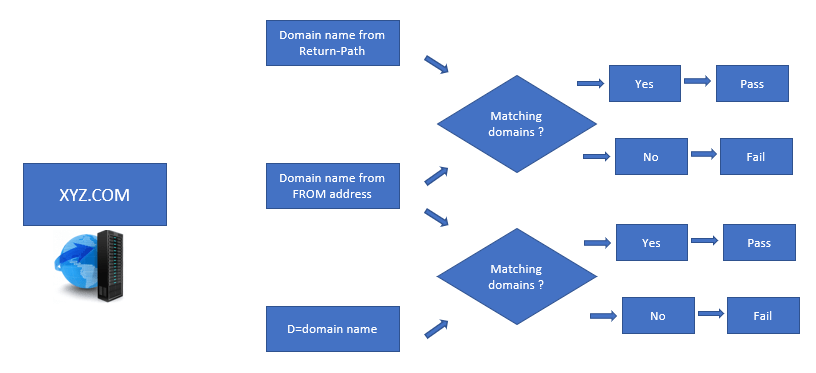
Recipient server will first extract the domain name from the Return-Path within the email header. Then Recipient server will extract domain name from FROM address and will match both domain names (domain name collected from Return-Path and FROM address). This is called SPF alignment. If both domain names are matching, SPF will pass. If domain names are not matching, SPF will fail. And if SPF alignment fails, recipient server will perform DKIM validation.
Recipient server will check the domain name within D= attribute, and will match that domain with the domain name extracted from the FROM address. D= is a value that is found within the DKIM signatures which indicates which domain has signed this particular email. If both domain names match, DKIM will pass else DKIM will fail. Now, if either SPF or DKIM check fails, recipient server will treat that email as per the action specified by the sending server within the DMARC record.
Create DMARC record for your domain
Below is a standard DMARC record.
"v=DMARC1; p=Reject; pct=100; rua=mailto:analyse@domain.com"Let’s break this record and let’s understand each component of the DMARC record.
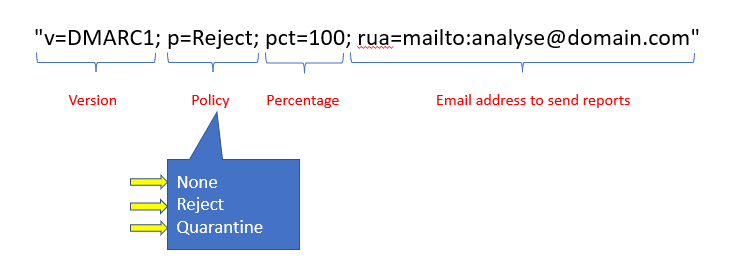
- V=DMARC1 indicates the version of DMARC record that sender email server is using.
- P= stands for Policy. Under policy we specify the action that recipient server will take in case SPF or DKIM fails on your email. Under policy, we can define 3 actions None, Reject, and Quarantine. If you have specified action None, that means recipient server will not take any action and email will be delivered to the recipient. If you specify Reject action, the recipient email server will reject this email if SPF or DKIM or both will fail. If policy is set to Quarantine, the recipient email server will redirect that email to their quarantine portal.
- PCT= is the percentage of the emails to which the domain owner would like to have its policy applied. If it is set to 100, that means all emails sent from this domain will have p= policy applied.
- RUA=mailto is the mailbox to which reports should be sent for further analysis.
Conclusion
In this blog you learnt what is DMARC record and how DMARC record works. You might like our other articles on How SPF Record works, How MX record works, and How DKIM record works.
If you found this article helpful and informative, please share it within your community and do not forget to share your feedback in the comments below. Please join us on our YouTube channel for the latest videos on Cloud technology and join our Newsletter for the early access of the blogs and updates.
Happy Learning!!
