Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication and Security Defaults
In this post we will understand what is Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication and Security Defaults. We will also learn what is the difference between Azure AD multi-factor authentication and security defaults.
Table of Contents
Watch the video
Watch this video to learn the difference between Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication and Security Defaults.
Azure AD Security Defaults
Microsoft has made security defaults available for everyone. When you create a new tenant, you get a free subscription of Azure Active Directory and Security Defaults are enabled by default.
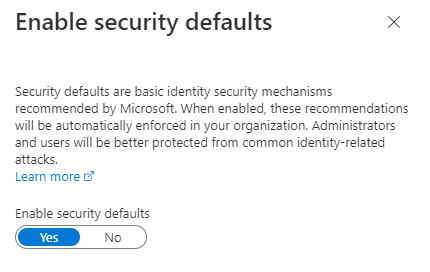
Security defaults is a free feature that helps you to protect accounts from being hacked. If security defaults are enabled, all of your users including Admin accounts will have to enroll themselves for Multi-Factor Authentication.
Pre-configured policies of security defaults
Security defaults have some of the pre-configured security policies, that help you to protect your organization identities from being hacked.
- When security defaults are enabled, all of the users of your tenant (including the administrator accounts) will have to register for multi-factor authentication. Users will have 14 days to register for multi-factor authentication. And after 14 days have passed, the users will not be able to login until the registration is completed.
- When security defaults are enabled in your tenant, all the legacy authentication protocols are disabled. Legacy authentication is a type of authentication request that is made by the clients that do not use modern authentication. For example Office 2010. Some other clients that use older email protocols, also use legacy authentication. For example, POP3, IMAP or SMTP. Legacy authentication doesn’t support Multi-Factor Authentication. Even if you have a Multi-Factor Authentication policy enabled on your tenant, an attacker can authenticate by using an older protocol, and can bypass Multi-Factor Authentication. So when security defaults are enabled in your tenant, all authentication requests made by an older protocol will be blocked.
- When security defaults are enabled, any user or administrator that is accessing the Azure portal, Azure PowerShell, or Azure CLI, will have to complete the multi-factor authentication.
So if you have a free Azure Active Directory subscription, you can use Security Defaults to increase the security for your identities.
Security defaults limitations
There are couple of limitations of using Security Defaults.
- Security defaults are enabled for all the users in your tenant. You can not enable security default for a set of users.
- When you enroll your account for multi-factor authentication using security defaults, you can only use Authenticator App as an authentication method. You cannot use other authentication methods like, SMS verification or voice call verification.
Disable security defaults in Azure AD
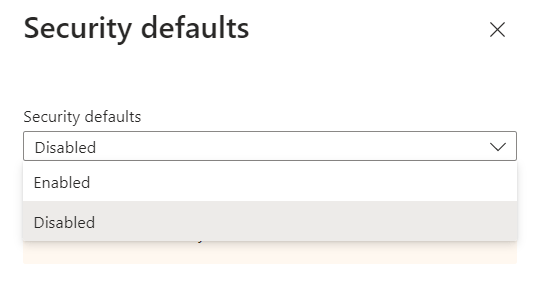
By default security defaults are enabled on every Azure AD tenant. To disable security defaults in Azure AD, login to Azure AD portal, click Properties and click Manage security defaults. Select Disabled (to disable security defaults) or Enabled (to enable security defaults).
Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication.
Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication is configured using Conditional Access policies. You can enable Azure AD MFA to all the users of your tenant or to a set of users. To use Azure AD MFA you need at least Azure Active Directory Premium P1 license. If you have Enterprise Mobility and security E3 license or Microsoft 365 E3, or Microsoft 365 Business Premium subscription, these licenses also include Azure AD Premium P1 license.
Enable Azure AD Multi Factor Authentication
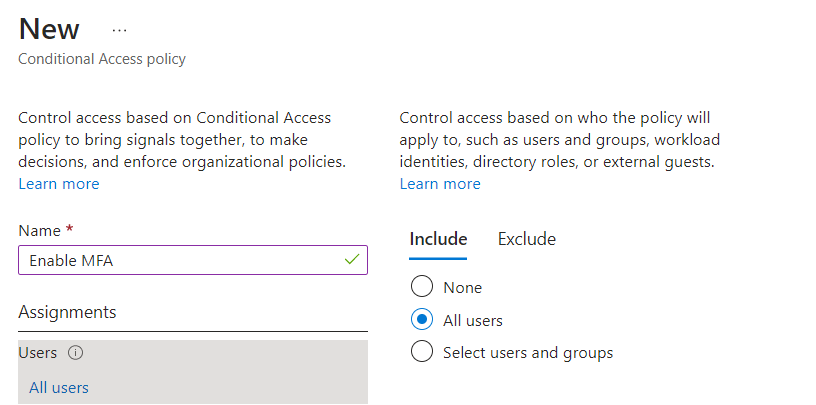
To Enable Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication using Condition Access policies, go to Azure AD portal, select Security, Conditional Access, click Policies and click New Policy.
Type a name for the policy that you want to create, under Assignments, select the users, groups, external users or the users on the basis of Directory Roles.
Under Access Controls, select Grant, click Grant Access, and check Require multifactor authentication.
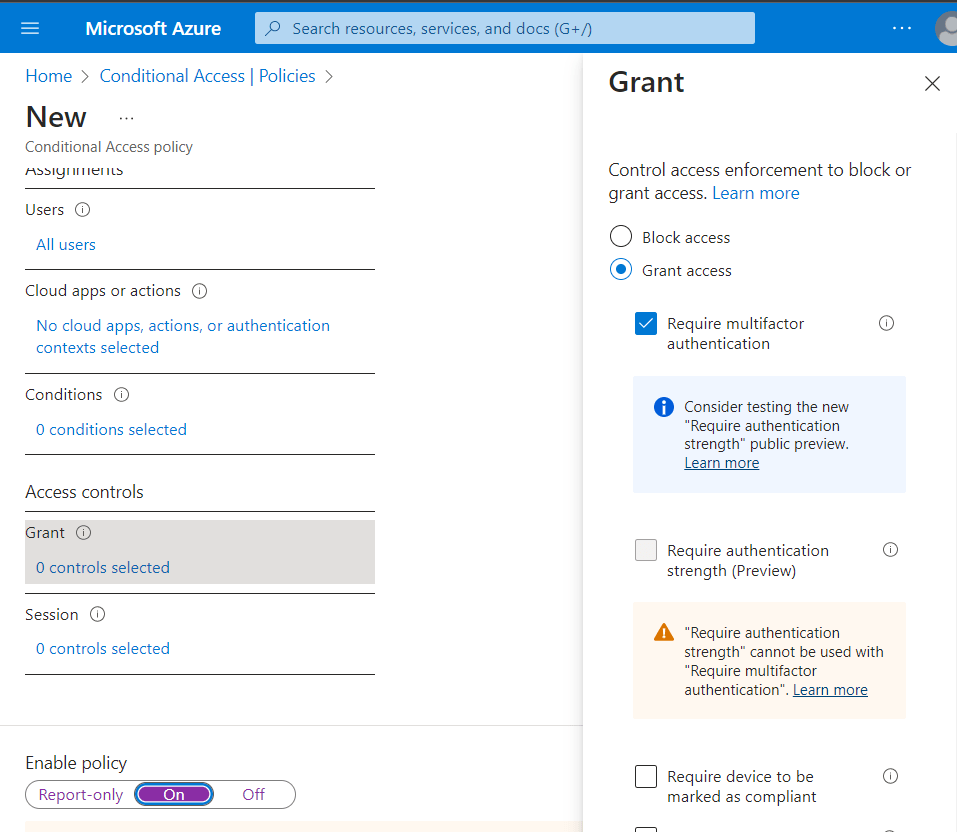
Select On to enable to this policy and click Create.
When users ()who are part of this policy, will try to login to Microsoft Online services, they will be prompted to enroll themselves for multi-factor authentication.
Azure MFA vs Security defaults
As we discussed, security defaults is a free feature of Azure Active Directory. To use security defaults you do not need any sort of license. When you create an Azure Active Directory tenant, you get security defaults automatically. On the other hand, if you want to use Azure AD MFA, you need at least Azure Active Directory Premium P1 license. If you have Enterprise Mobility and security E3 license or Microsoft 365 E3, or Microsoft 365 Business Premium subscription, these licenses also include Azure AD Premium P1 license.
Security defaults can be enabled for all the users of your tenant. You can not select a group of users for which you want to enable multi-factor authentication. But you can enable Azure AD MFA for all the users, or to a set of users.
If you are using security defaults, users can use only the Microsoft Authenticator App as an authentication method. But Azure AD MFA supports multiple authentication methods like, Authenticator app, SMS verification, or phone call verification.
Security defaults are very easy to implement and does not require any sort of configuration at the admin level. But Azure AD MFA is configured using Conditional Access policies.
Happy Learning!!
