Mastering Conditional Access Policies: A Comprehensive Guide to Components and Best Practices
Unlock the full potential of Conditional Access policies with our in-depth blog. Discover the crucial components, implementation strategies, and best practices for maximizing security while enabling seamless user access. Dive into the intricate world of Conditional Access and learn how to craft policies tailored to your organization’s needs.
Table of Contents
Watch the video
To learn Conditional Access policies in depth, please watch below videos on our YouTube channel.
A deep dive session on Conditional Access policies
Configure Conditional Access policies
What are Conditional Access policies
In nutshell, Conditional Access policies are if-then statements. For example If an administrator wants to access Azure portal, he needs to enroll for Multi-Factor Authentication, and then he will get access to the Azure Portal.
One important thing that you should know is, Conditional Access policies are enforced after user logs-in to an application. That means, when a user will sign-in using his username and password, and when this user will be authenticated by Azure Active Directory, only then conditional access policies will be applied on this user.
Let’s say if the user didn’t type his password correctly. So in that case, the authentication will fail and conditional access policies will not be enforced on this user.
Conditional Access policies signals
Conditional Access policies use Signals to determine the access. These signals can be users, or groups (e.g., You might have created a policy targeted to users or groups that is giving access to the admin roles). Signals can be a location or an IP address. You can create Trusted IP Address Range, that can be used when making policy decisions.
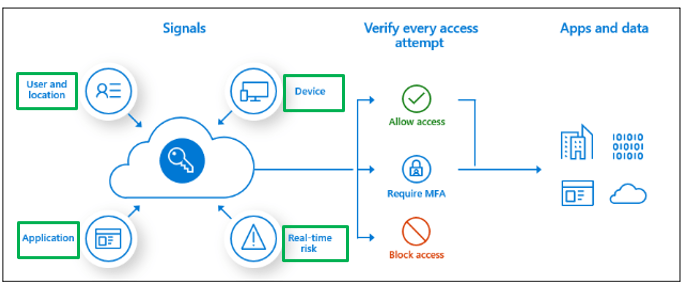
Signals can be a Device, from where user is accessing an application. You can create device-based filters in conditional access policy that will be targeting specific devices.
Signals can be an application, that user is trying to access. You can create Conditional Access Policy on the basis of what application users can access.
You can create conditional Access Policies to identify risky-sign-in behavior.
So basis on these signals, you create conditions, and then you specify the action. Like, whether access should be allowed or it should be blocked. And basis on the action, either access to the application is provided or it is denied.
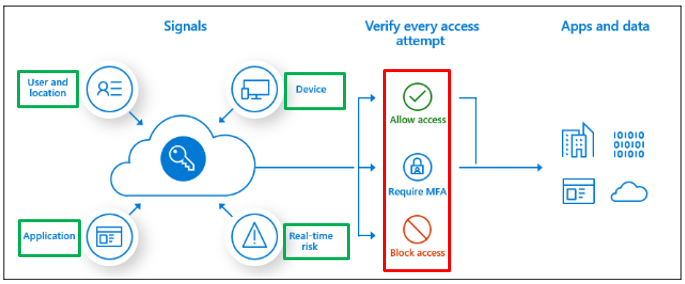
Components of Conditional Access policies
Conditional Access Policies have 4 major components. Assignments, Cloud Apps or Actions, Conditions, and Access Controls.
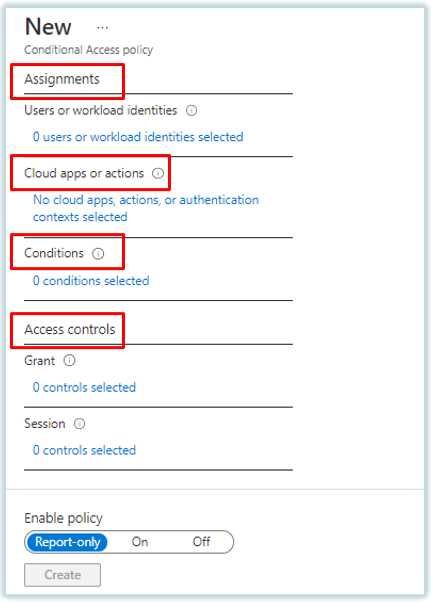
We will discuss these components in detail, before we start configuring conditional access policies.
1. Assignments: The assignments portion controls to whom you want to assign the policy. Under Assignments, you can either include or exclude the users and groups. You can include or exclude all users or a set of users using a security group, you can add directory roles, or you can include or exclude external guest users.
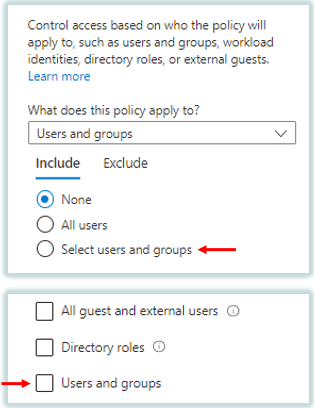
Under Include section If you select None, that means no users are selected. If you select All Users, that means all the users of your Azure AD Tenant will be added under this policy including External users as well.
If you want to add specific users or a set of users, you will click Select users and groups. And then you can select the users or groups manually as per your requirement.
If you want to apply this policy to the guest users or external users, you will select All guest and external users.
If you want to apply this policy on the users on the basis of Azure AD roles, for example, if you want to apply this policy on the Admins who have Global Administrator role assigned, in that case you will select Directory roles.
And If you want to apply Azure AD conditional access policies on specific users, or you want to apply a policy on a security group, you will select Users and Groups.
You can also exclude users or groups from conditional access policies.
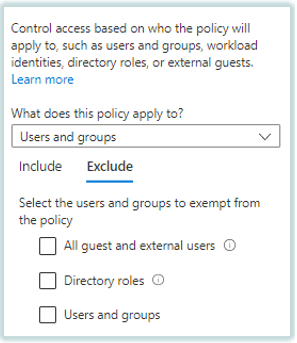
If you want to exclude users, guest users, or groups from a particular policy, you will make all these changes under Exclude section. When you exclude a user or group from a policy, that policy will not take any action on that particular object. This is similar to the transport rules (mail flow rules) in Exchange Online.
2. Cloud Apps or Actions: Next component of Conditional Access Policy is Cloud Apps or Actions. Under this component you can select cloud applications, user actions, and authentication context.
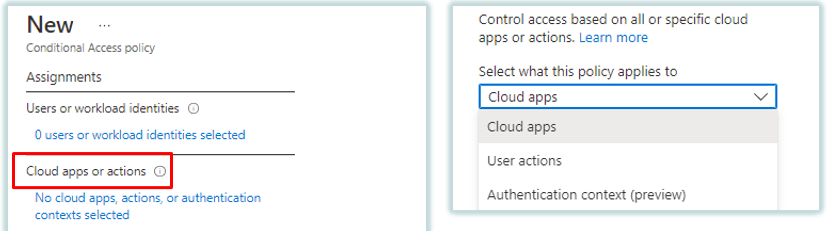
If you want to apply a conditional access policy on cloud applications, you will select cloud apps. Under cloud apps, you can select multiple cloud applications. Like, Office 365 application, Exchange Online, SharePoint Online, Intune, Devops, Yammer, Microsoft Teams and so on.
Under User Actions you can specify the task, that can be performed by a user. As of now conditional access policy supports 2 user actions. Register Security Information and Register or Join devices.
If you select Register Security Information, this action will allow Conditional Access policy to enforce when users will try to register their security information. For example while configuring MFA or self-service password reset. And if you select Register or join devices, this action will allow administrators to enforce a Conditional Access policy when users will try to register or join their devices to Azure Active Directory.
Next is Authentication Context. This option can be used to further secure your data or the applications. These applications can be custom application, SharePoint applications, or the applications those are protected by Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps.
3. Conditions: The next component of Azure AD Conditional Access policies is Conditions.
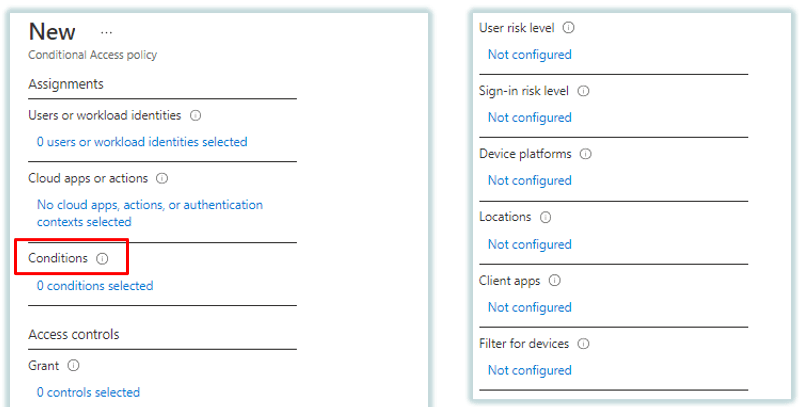
Under Conditions, an administrator can add conditions like, device platform, location, or client applications. So let’s discuss these conditions in detail.
User risk level is a calculation of possibility that an identity has been compromised. And basis on this calculation, administrators can enforce Conditional Access policies to either block the access or to allow the access with MFA.
Next condition is Sign-in Risk level. This policy is a calculation of the possibility that the sign-in attempt that was done on an account, is not performed by the owner of the account. So basis on this calculation, admins can either block the access or they can allow the access with MFA.
Next is Device Platforms. Under this condition you can include or exclude the devices basis on their Operating System. Conditional Access policies support Android operating system, iOS, Windows, Mac operating system, and Linux.
Under Locations you can include or exclude a country, a region, or a public IP address.
Next condition is Client Apps. Under this condition you can enforce conditional access policies on the applications. Like, Outlook client, browsers, Exchange Active Sync clients, or the applications that use IMAP and POP protocols.
Under Filter for devices you can include or exclude the devices basis on the filter.
4. Access Controls: The next component of Azure AD Conditional Access policies is Access Controls. Under access controls, administrators can Grant or Block the access.
And using Session, we can let Azure Active Directory to pass the device information to the cloud Apps. The device information allows cloud apps to know, if the connection is coming from a compliant or domain-joined device. And basis on the device information, the access to the applications can be rejected or it is approved.
Under Enable Policy, you can select if you want to enforce the policy or you want to disable the policy. Or you want to monitor the policy first and then you want to apply it. So if you select OFF, that means policy is disabled. If you select ON, that means policy is enabled and it is getting enforced as per the conditions and actions specified within the policy.
And if you want to evaluate the impact of Conditional Access policy before enabling it, you can select Report Only. And you can refer to the Sign-in logs to monitor the action taken by conditional access policy.
So using all these components you can create a conditional access policy in Azure Active Directory.
Related articles
We welcome you to browse our other blogs on Azure Active Directory:
What is Azure Active Directory
What is Self Service Password Reset
A Guide to Passwordless Authentication Using Authenticator App
Top 40+ Azure Active Directory interview questions and answers
Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication and Security Defaults
Users and Groups in Azure AD
Simple steps to add domain in Azure Active Directory
Happy Learning!!
